
Austria Country Profile
Key Facts of Austria
| Government type: | federal parliamentary republic |
| Capital: | Vienna |
| Languages: | German (official nationwide) 88.6%, Turkish 2.3%, Serbian 2.2%, Croatian (official in Burgenland) 1.6%, other (includes Slovene, official in southern Carinthia, and Hungarian, official in Burgenland) 5.3% (2001 est.) |
Austria Demographic Data
Ethnic Groups in Austria(2018 est.)
Religious Groups in Austria (2021 est.)
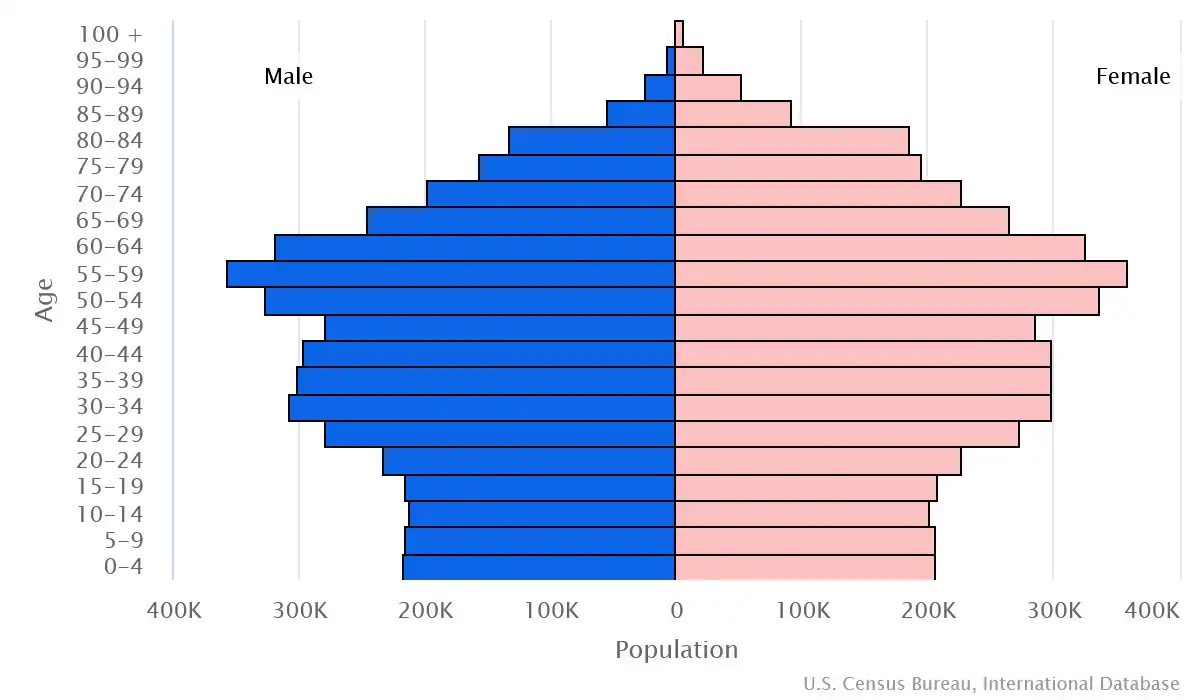
Age pyramid of Austria
Austria Economy Statistics
Economic overview of Austria
one of the strongest EU and euro economies; diversified trade portfolios and relations; enormous trade economy; Russian energy dependence, but investing in alternative energy; aging labor force but large refugee population; large government debt
Austria Real GDP (purchasing power parity) in Billion $
Austria Real GDP per capita in $
Austria's Exports & Imports in billion $
Top 5 Import Partnerin 2022 (61%) of Austria
Top 5 Import Commodities in 2022 of Austria
- cars 🚗
- refined petroleum ⛽
- gold 💰
- garments 👕
- broadcasting equipment 📡
Top 5 Export Partnerin 2022 (52%) of Austria
Top 5 Export Commodities in 2022 of Austria
- cars 🚗
- packaged medicine 💊
- vaccines 💉
- plastic products ♻️
- electricity ⚡
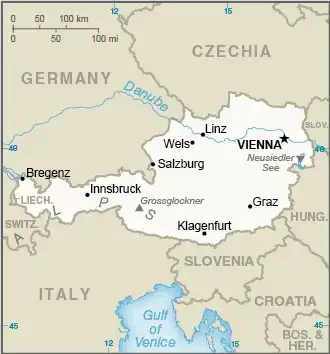
Geography of Austria
Map of Austria
Land and Water Distrubtion of Austria
Natural Resources of Austria
- oil 🛢️
- coal ⚫
- lignite 🪨
- timber 🌲
- iron ore ⛓️
- copper 🟧🪙
- zinc 🔩
- antimony 🏺
- magnesite 🏔️
- tungsten 🔧
- graphite ✏️
- salt 🧂
- hydropower 💧⚡
Climate inAustria
temperate; continental, cloudy; cold winters with frequent rain and some snow in lowlands and snow in mountains; moderate summers with occasional showers
History of Austria - a Summary
Once the center of power for the large Austro-Hungarian Empire, Austria was reduced to a small republic after its defeat in World War I. Nazi Germany annexed Austria in 1938, and the victorious Allies then occupied the country in 1945. As a result, Austria's status remained unclear for a decade after World War II, until a State Treaty signed in 1955 ended the occupation, recognized Austria's independence, and forbade unification with Germany. A constitutional law that same year declared the country's "perpetual neutrality" as a condition for Soviet military withdrawal. Austria joined the EU in 1995, but the obligation to remain neutral kept it from joining NATO, although the country became a member of NATO's Partnership for Peace program in 1995. Austria entered the EU Economic and Monetary Union in 1999.
