Bangladesh Country Profile
Key Facts of Bangladesh
| Government type: | parliamentary republic |
| Capital: | Dhaka |
| Languages: | Bangla 98.8% (official, also known as Bengali), other 1.2% (2011 est.) |
Bangladesh Demographic Data
Ethnic Groups in Bangladesh(2022 est.)
Religious Groups in Bangladesh (2022 est.)
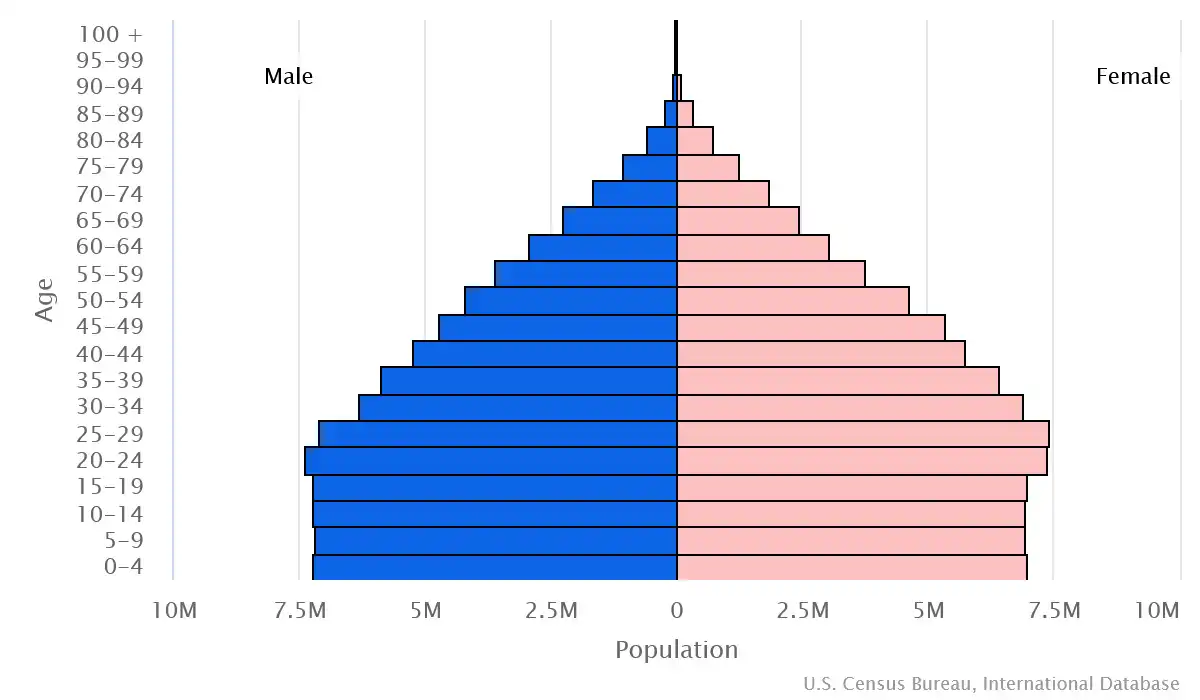
Age pyramid of Bangladesh
Bangladesh Economy Statistics
Economic overview of Bangladesh
one of the fastest growing emerging market economies; strong economic rebound following COVID-19; significant poverty reduction; exports dominated by textile industry; weakened exports and remittances resulted in declining foreign exchange reserves and 2022 IMF loan request
Bangladesh Real GDP (purchasing power parity) in Billion $
Bangladesh Real GDP per capita in $
Bangladesh's Exports & Imports in billion $
Top 5 Import Partnerin 2022 (65%) of Bangladesh
Top 5 Import Commodities in 2022 of Bangladesh
- refined petroleum ⛽
- cotton fabric 🧵
- cotton 🧵
- fabric 👕🧶
- fertilizers 💩
Top 5 Export Partnerin 2022 (55%) of Bangladesh
Top 5 Export Commodities in 2022 of Bangladesh
- garments 👕
- footwear 👞
- fabric 👕🧶
- textiles 🧶
- jute yarn 🧵
Geography of Bangladesh
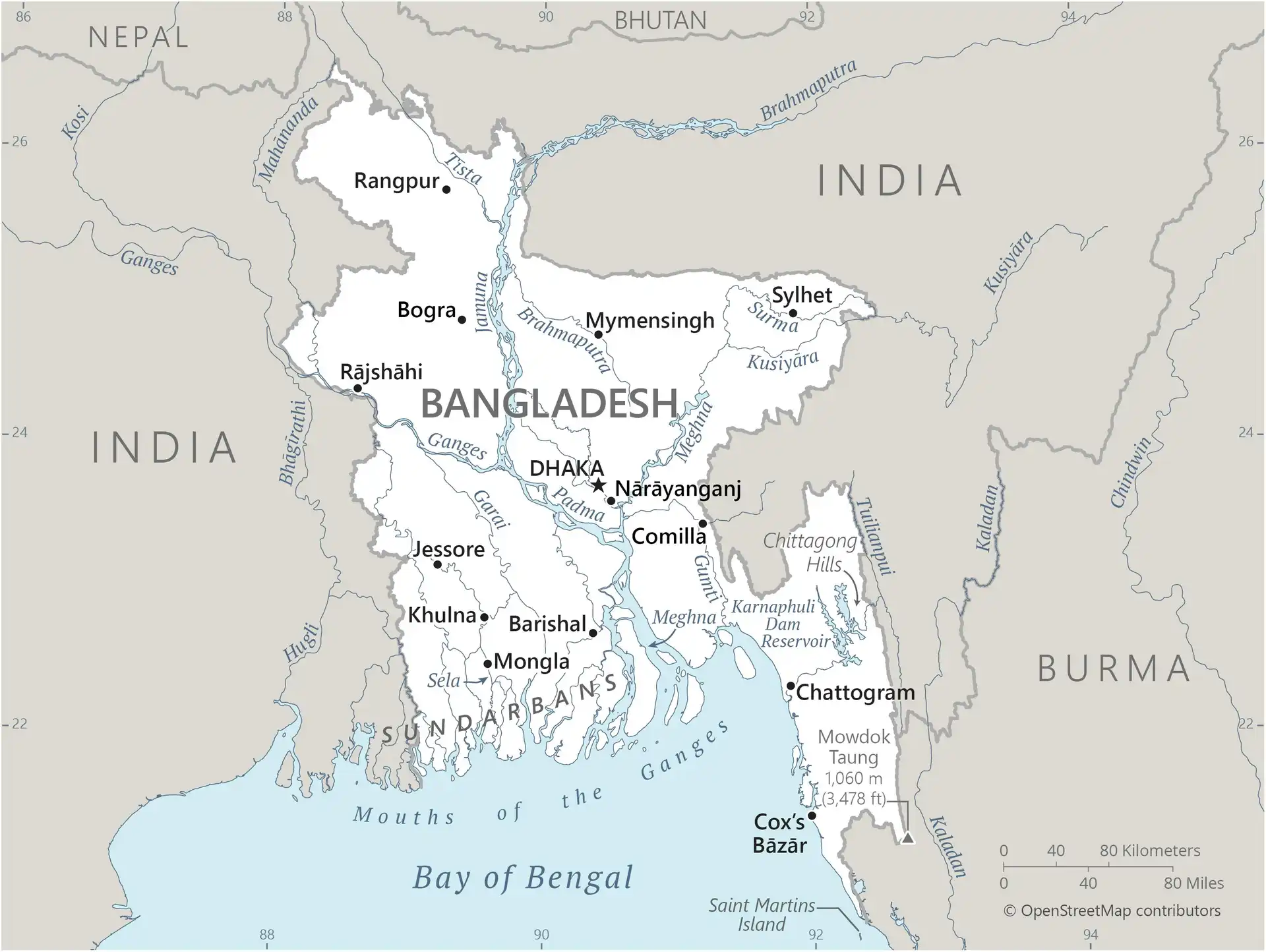
Map of Bangladesh
Land and Water Distrubtion of Bangladesh
Natural Resources of Bangladesh
- natural gas 💨
- arable land 🌱
- timber 🌲
- coal ⚫
Climate inBangladesh
tropical; mild winter (October to March); hot, humid summer (March to June); humid, warm rainy monsoon (June to October)
History of Bangladesh - a Summary
The huge delta region at the confluence of the Ganges and Brahmaputra River systems -- now referred to as Bangladesh -- was a loosely incorporated outpost of various empires for much of the first millennium A.D. Muslim conversions and settlement in the region began in the 10th century, primarily from Arab and Persian traders and preachers. Europeans established trading posts in the area in the 16th century. Eventually the area known as Bengal, which is primarily Hindu in the western section and mostly Muslim in the eastern half, became part of British India. After the partition of India in 1947, the Muslim-majority area became East Pakistan. Calls for greater autonomy and animosity between the eastern and western areas of Pakistan led to a Bengali independence movement. That movement, led by the Awami League (AL) and supported by India, won the independence war for Bangladesh in 1971.
The military overthrew the post-independence AL government in 1975, the first of a series of military coups that resulted in a military-backed government and the subsequent creation of the Bangladesh Nationalist Party (BNP) that took power in 1979. That government also ended in a coup in 1981, followed by military-backed rule until democratic elections were held in 1991. The BNP and AL alternated in power from 1991 to 2008, with the exception of a military-backed, emergency caretaker regime in 2007. The country returned to fully democratic rule in 2008 with the election of the AL and Prime Minister Sheikh HASINA. With the help of international development assistance, Bangladesh is on track to graduate from the UN’s Least Developed Countries (LDC) list in 2026.
The economy has grown at an annual average of about 6.25% for the last two decades. Poverty declined from 11.8 percent in 2010 to 5.0 percent in 2022, based on the international poverty line of $2.15 a day (using 2017 Purchasing Power Parity exchange rate). Moreover, human development outcomes improved along many dimensions. The country made a rapid recovery from the COVID-19 pandemic, but faces several economic challenges.
