Barbados Country Profile
Key Facts of Barbados
| Government type: | parliamentary republic; a Commonwealth realm |
| Capital: | Bridgetown |
| Languages: | English (official), Bajan (English-based creole language, widely spoken in informal settings) |
Barbados Demographic Data
Ethnic Groups in Barbados(2010 est.)
Religious Groups in Barbados (2010 est.)
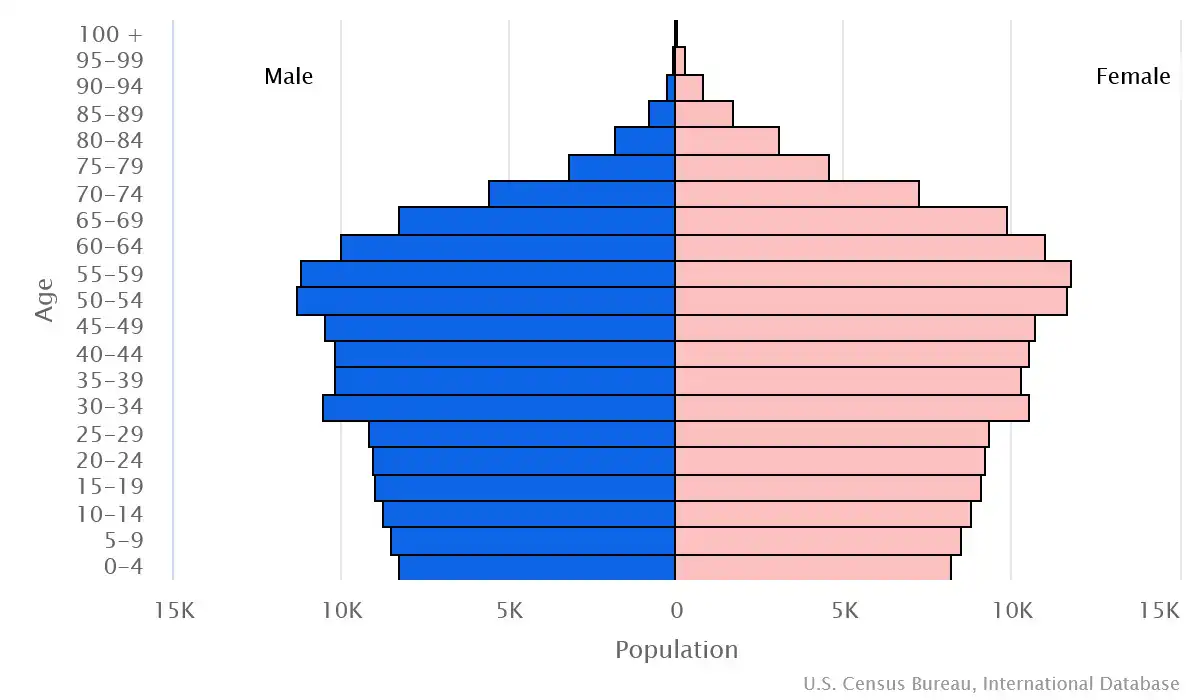
Age pyramid of Barbados
Barbados Economy Statistics
Economic overview of Barbados
high-income Eastern Caribbean economy; high standard of living among regional peers; key tourism, construction, and financial sectors driving recent GDP growth; declining but still very high public debt leading to IMF support programs; susceptible to natural disasters and reliance on import partners
Barbados Real GDP (purchasing power parity) in Billion $
Barbados Real GDP per capita in $
Barbados's Exports & Imports in billion $
Top 5 Import Partnerin 2022 (66%) of Barbados
Top 5 Import Commodities in 2022 of Barbados
- refined petroleum ⛽
- plastic products ♻️
- cars 🚗
- railway cargo containers 🚂
- packaged medicine 💊
Top 5 Export Partnerin 2022 (57%) of Barbados
Top 5 Export Commodities in 2022 of Barbados
- liquor 🍷
- packaged medicine 💊
- ships 🚢
- paper labels 📄
- baked goods 🍞
Geography of Barbados
Map of Barbados
Land and Water Distrubtion of Barbados
Natural Resources of Barbados
- petroleum 🛢️
- fish 🐟
- natural gas 💨
Climate inBarbados
tropical; rainy season (June to October)
History of Barbados - a Summary
Barbados was uninhabited when first settled by the British in 1627. Enslaved Africans worked the sugar plantations established on the island, which initially dominated the Caribbean sugar industry. By 1720, Barbados was no longer a dominant force within the sugar industry, having been surpassed by the Leeward Islands and Jamaica. Slavery was abolished in 1834. The Barbadian economy remained heavily dependent on sugar, rum, and molasses production through most of the 20th century. The gradual introduction of social and political reforms in the 1940s and 1950s led to independence from the UK in 1966. In the 1990s, tourism and manufacturing surpassed the sugar industry in economic importance. Barbados became a republic in 2021, with the former Governor-General Sandra MASON elected as the first president.
