
Croatia Country Profile
Key Facts of Croatia
| Government type: | parliamentary republic |
| Capital: | Zagreb |
| Languages: | Croatian (official) 95.2%, Serbian 1.2%, other 3.1% (including Bosnian, Romani, Albanian, and Italian) unspecified 0.5% (2021 est.) |
Croatia Demographic Data
Ethnic Groups in Croatia(2021 est.)
Religious Groups in Croatia (2021 est.)
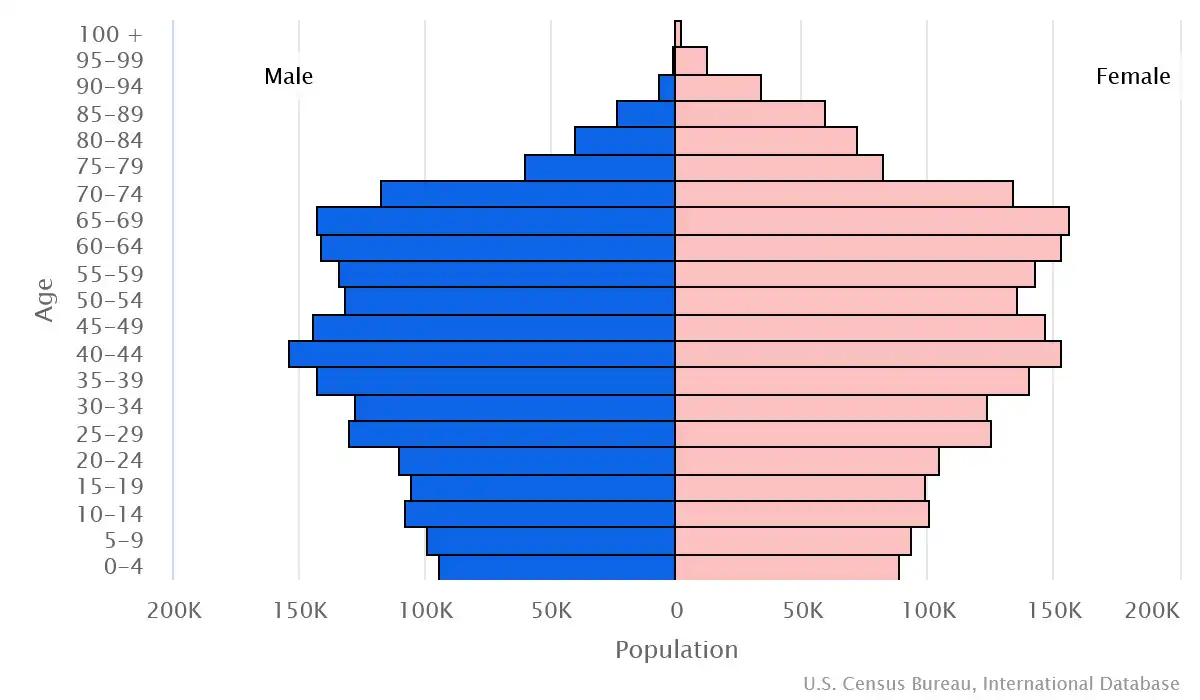
Age pyramid of Croatia
Croatia Economy Statistics
Economic overview of Croatia
tourism-based economy that was one of the hardest hit by COVID-19 economic disruptions; newest euro user since 2023, helping recover from a 6-year recession; public debt increases due to COVID-19 and stimulus packages; weak exports; continuing emigration; new liquefied natural gas import terminal
Croatia Real GDP (purchasing power parity) in Billion $
Croatia Real GDP per capita in $
Croatia's Exports & Imports in billion $
Top 5 Import Partnerin 2022 (51%) of Croatia
Top 5 Import Commodities in 2022 of Croatia
- natural gas 💨
- refined petroleum ⛽
- electricity ⚡
- garments 👕
- cars 🚗
Top 5 Export Partnerin 2022 (54%) of Croatia
Top 5 Export Commodities in 2022 of Croatia
- refined petroleum ⛽
- electricity ⚡
- natural gas 💨
- garments 👕
- wood 🌲
Geography of Croatia
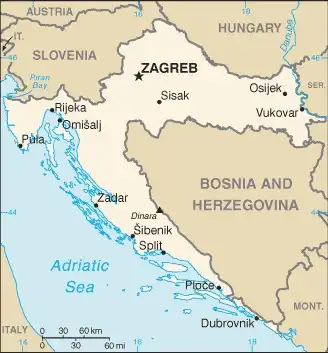
Map of Croatia
Land and Water Distrubtion of Croatia
Natural Resources of Croatia
- oil 🛢️
- some coal ⚫
- bauxite 🪨
- low-grade iron ore ⛓️
- calcium 🦴
- gypsum ⚪🪨
- natural asphalt 🛢️
- silica 🪨
- mica 🪨
- clays 🧱
- salt 🧂
- hydropower 💧⚡
Climate inCroatia
Mediterranean and continental; continental climate predominant with hot summers and cold winters; mild winters, dry summers along coast
History of Croatia - a Summary
The lands that today comprise Croatia were part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire until the end of World War I. In 1918, the Croats, Serbs, and Slovenes formed a kingdom known after 1929 as Yugoslavia. Following World War II, Yugoslavia became a federal independent communist state consisting of six socialist republics, including Croatia, under the strong hand of Josip Broz, aka TITO. Although Croatia declared its independence from Yugoslavia in 1991, it took four years of sporadic, but often bitter, fighting before Yugoslav forces were cleared from Croatian lands, along with a majority of Croatia's ethnic Serb population. Under UN supervision, the last Serb-held enclave in eastern Slavonia was returned to Croatia in 1998. The country joined NATO in 2009 and the EU in 2013. In January 2023, Croatia further integrated into the EU by joining the Eurozone and the Schengen Area.
