Czechia Country Profile
Key Facts of Czechia
| Government type: | parliamentary republic |
| Capital: | Prague |
| Languages: | Czech (official) 88.4%, Slovak 1.5%, other 2.6%, unspecified 7.2% (2021 est.) |
Czechia Demographic Data
Ethnic Groups in Czechia(2021 est.)
Religious Groups in Czechia (2021 est.)
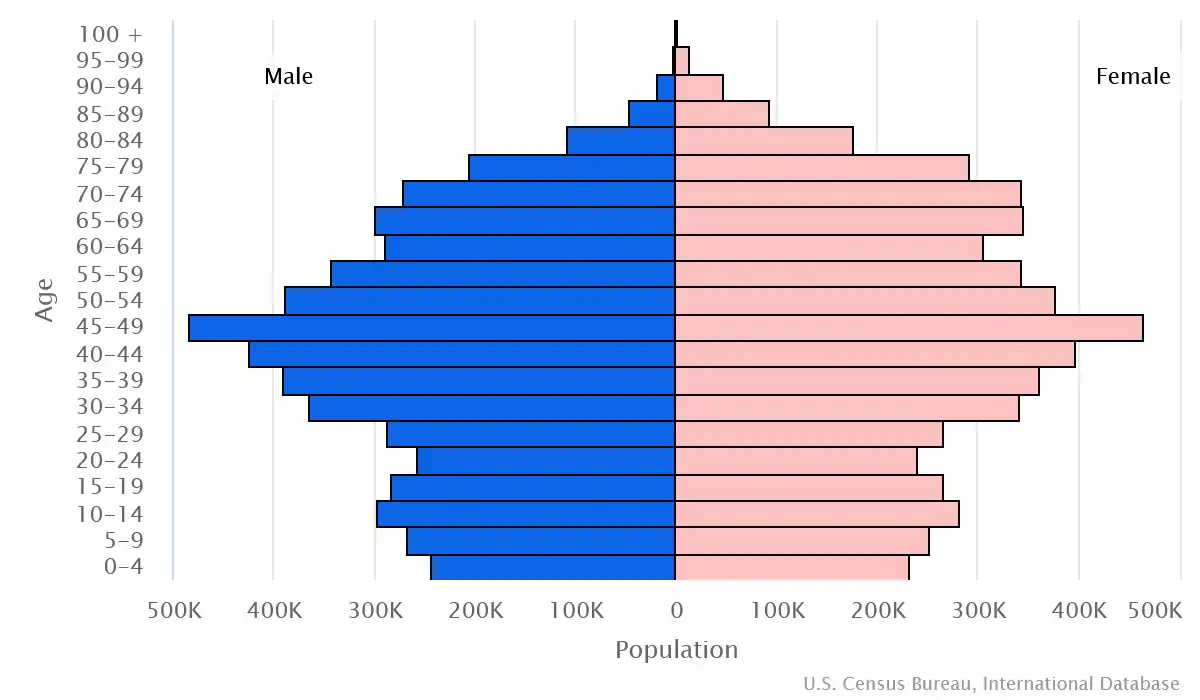
Age pyramid of Czechia
Czechia Economy Statistics
Economic overview of Czechia
high-income, diversified EU economy; manufacturing-oriented exporter led by automotive industry; growth stalled by inflation and energy supply disruption; business-friendly regulatory frameworks; tight labor market with low unemployment; seeking reforms to support decarbonization and improve energy efficiency
Czechia Real GDP (purchasing power parity) in Billion $
Czechia Real GDP per capita in $
Czechia's Exports & Imports in billion $
Top 5 Import Partnerin 2022 (57%) of Czechia
Top 5 Import Commodities in 2022 of Czechia
- broadcasting equipment 📡
- vehicle parts/accessories 🛠️🚗
- natural gas 💨
- machine parts ⚙️
- plastic products ♻️
Top 5 Export Partnerin 2022 (57%) of Czechia
Top 5 Export Commodities in 2022 of Czechia
- cars 🚗
- vehicle parts/accessories 🛠️🚗
- broadcasting equipment 📡
- computers 💻
- plastic products ♻️
Geography of Czechia
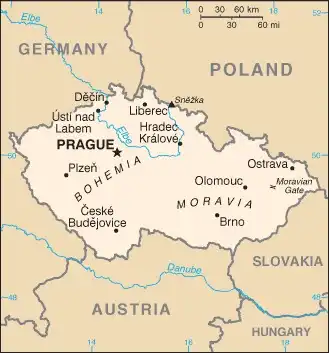
Map of Czechia
Land and Water Distrubtion of Czechia
Natural Resources of Czechia
- hard coal ⚫
- soft coal ⚫
- kaolin 🪨
- clay 🧱
- graphite ✏️
- timber 🌲
- arable land 🌱
Climate inCzechia
temperate; cool summers; cold, cloudy, humid winters
History of Czechia - a Summary
At the close of World War I, the Czechs and Slovaks of the former Austro-Hungarian Empire merged to form Czechoslovakia, a parliamentarian democracy. During the interwar years, having rejected a federal system, the new country's predominantly Czech leaders were frequently preoccupied with meeting the increasingly strident demands of other ethnic minorities within the republic, most notably the Slovaks, the Sudeten Germans, and the Ruthenians (Ukrainians). On the eve of World War II, Nazi Germany occupied the territory that today comprises Czechia, and Slovakia became an independent state allied with Germany. After the war, a reunited but truncated Czechoslovakia (less Ruthenia) fell within the Soviet sphere of influence when the pro-Soviet Communist party staged a coup in February 1948. In 1968, an invasion by fellow Warsaw Pact troops ended the efforts of the country's leaders to liberalize communist rule and create "socialism with a human face," ushering in a period of repression known as "normalization." The peaceful "Velvet Revolution" swept the Communist Party from power at the end of 1989 and inaugurated a return to democratic rule and a market economy. On 1 January 1993, the country underwent a nonviolent "velvet divorce" into its two national components, the Czech Republic and Slovakia. The Czech Republic joined NATO in 1999 and the European Union in 2004. The country formally added the short-form name Czechia in 2016, while also continuing to use the full form name, the Czech Republic.
