
Dominican Republic Country Profile
Key Facts of Dominican Republic
| Government type: | presidential republic |
| Capital: | Santo Domingo |
| Languages: | Spanish (official) |
Dominican Republic Demographic Data
Ethnic Groups in Dominican Republic(2014 est.)
Religious Groups in Dominican Republic (2023 est.)
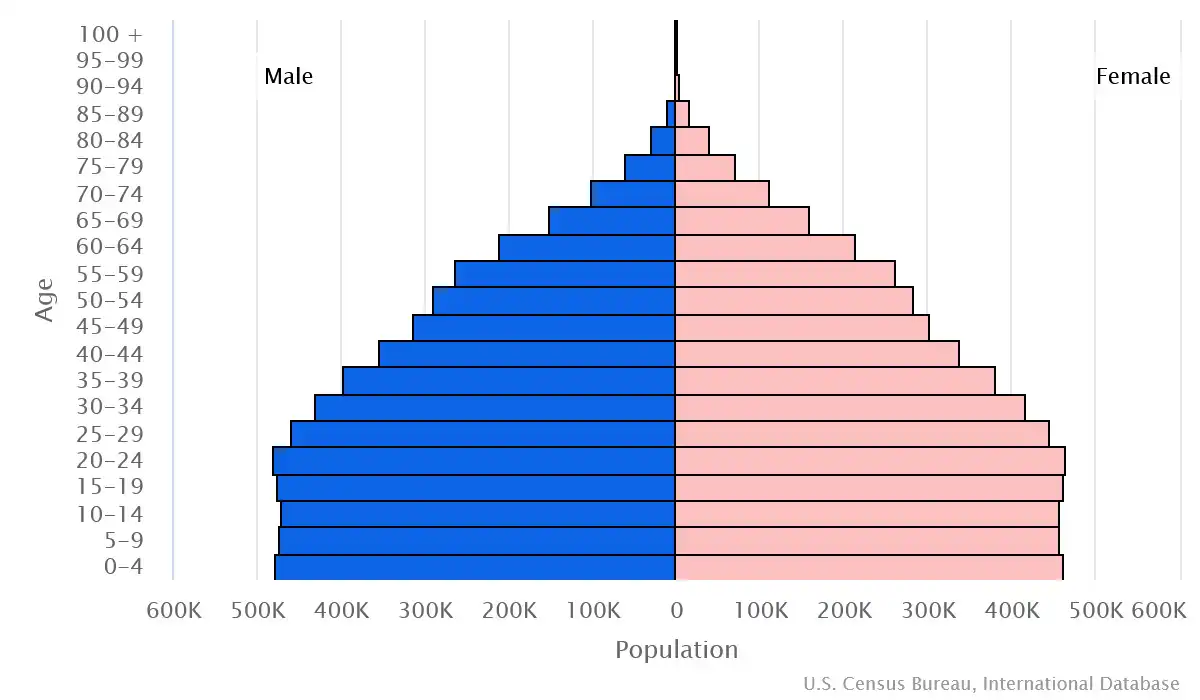
Age pyramid of Dominican Republic
Dominican Republic Economy Statistics
Economic overview of Dominican Republic
surging middle-income tourism, construction, mining, and telecommunications OECS economy; major foreign US direct investment and free-trade zones; developing local financial markets; improving debt management; declining poverty
Dominican Republic Real GDP (purchasing power parity) in Billion $
Dominican Republic Real GDP per capita in $
Dominican Republic's Exports & Imports in billion $
Top 5 Import Partnerin 2022 (69%) of Dominican Republic
Top 5 Import Commodities in 2022 of Dominican Republic
- refined petroleum ⛽
- natural gas 💨
- cars 🚗
- plastic products ♻️
- crude petroleum 🛢️
Top 5 Export Partnerin 2022 (71%) of Dominican Republic
Top 5 Export Commodities in 2022 of Dominican Republic
- medical instruments ⚕️
- gold 💰
- tobacco 🚬
- power equipment 🔋
- garments 👕
Geography of Dominican Republic
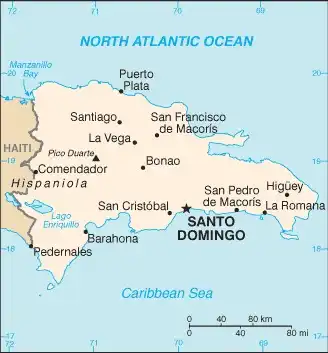
Map of Dominican Republic
Land and Water Distrubtion of Dominican Republic
Natural Resources of Dominican Republic
- nickel 🪙
- bauxite 🪨
- gold 💰
- silver 🪙
- arable land 🌱
Climate inDominican Republic
tropical maritime; little seasonal temperature variation; seasonal variation in rainfall
History of Dominican Republic - a Summary
The Taino -- indigenous inhabitants of Hispaniola prior to the arrival of Europeans -- divided the island now known as the Dominican Republic and Haiti into five chiefdoms and territories. Christopher COLUMBUS explored and claimed the island on his first voyage in 1492; it became a springboard for Spanish conquest of the Caribbean and the American mainland. In 1697, Spain recognized French dominion over the western third of the island, which in 1804 became Haiti. The remainder of the island, by then known as Santo Domingo, sought to gain its own independence in 1821, but the Haitians conquered and ruled it for 22 years; it finally attained independence as the Dominican Republic in 1844. In 1861, the Dominicans voluntarily returned to the Spanish Empire, but two years later, they launched a war that restored independence in 1865.
A legacy of unsettled and mostly non-representative rule followed, capped by the dictatorship of Rafael Leonidas TRUJILLO from 1930 to 1961. Juan BOSCH was elected president in 1962 but was deposed in a military coup in 1963. In 1965, the US led an intervention in the midst of a civil war sparked by an uprising to restore BOSCH. In 1966, Joaquin BALAGUER defeated BOSCH in the presidential election. BALAGUER maintained a tight grip on power for most of the next 30 years, until international reaction to flawed elections forced him to curtail his term in 1996. Since then, regular competitive elections have been held.
