
Ethiopia Country Profile
Key Facts of Ethiopia
| Government type: | federal parliamentary republic |
| Capital: | Addis Ababa |
| Languages: | Oromo (official regional working language) 33.8%, Amharic (official national language) 29.3%, Somali (official regional working language) 6.2%, Tigrigna (Tigrinya) (official regional working language) 5.9%, Sidamo 4%, Wolaytta 2.2%, Gurage 2%, Afar (official regional working language) 1.7%, Hadiyya 1.7%, Gamo 1.5%, Gedeo 1.3%, Opuuo 1.2%, Kafa 1.1%, other 8.1%, English (2007 est.) |
Ethiopia Demographic Data
Ethnic Groups in Ethiopia(2022 est.)
Religious Groups in Ethiopia (2016 est.)
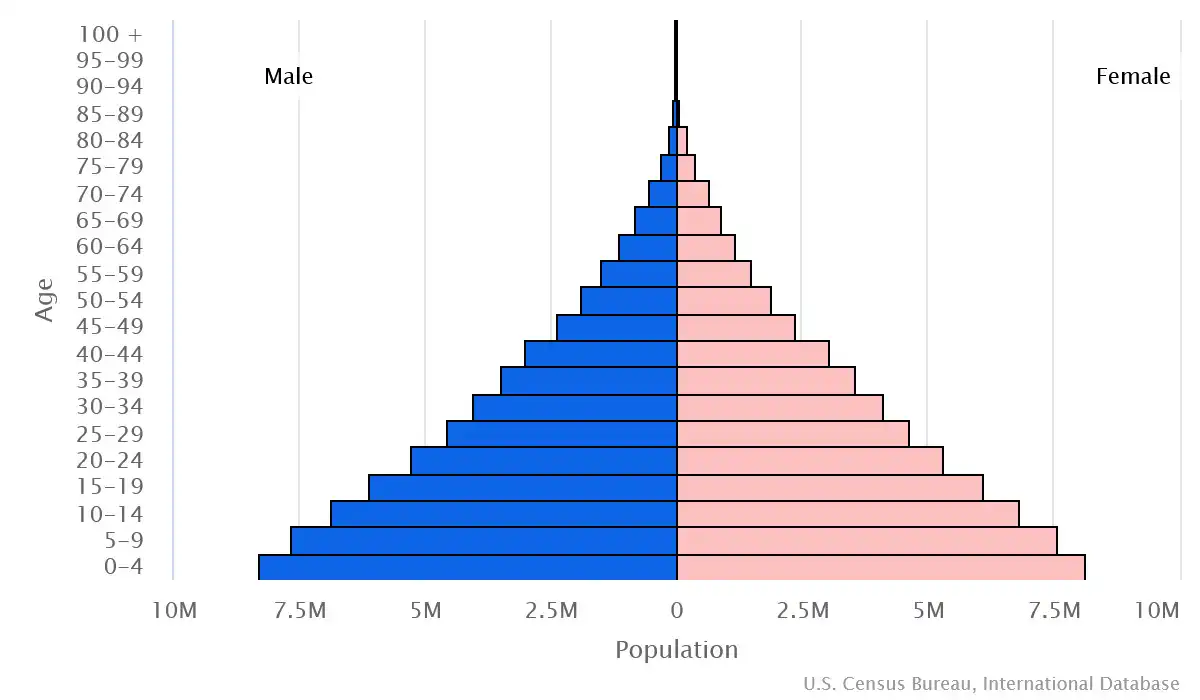
Age pyramid of Ethiopia
Ethiopia Economy Statistics
Economic overview of Ethiopia
growing Horn of Africa construction- and services-based economy; port access via Djibouti and Eritrea; widespread but declining poverty; COVID-19, locust invasion, and Tigray crisis disruptions; public investment increases; second largest African labor force
Ethiopia Real GDP (purchasing power parity) in Billion $
Ethiopia Real GDP per capita in $
Ethiopia's Exports & Imports in billion $
Top 5 Import Partnerin 2022 (51%) of Ethiopia
Top 5 Import Commodities in 2022 of Ethiopia
- wheat 🌾
- refined petroleum ⛽
- fertilizers 💩
- vaccines 💉
- palm oil 🛢️
Top 5 Export Partnerin 2022 (48%) of Ethiopia
Top 5 Export Commodities in 2022 of Ethiopia
- coffee ☕
- gold 💰
- garments 👕
- cut flowers 💐
- vegetables 🥦
Geography of Ethiopia
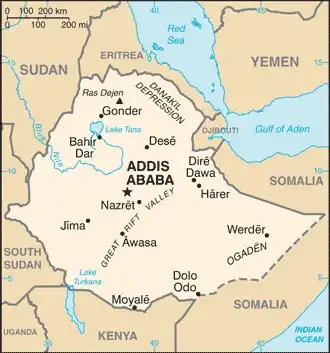
Map of Ethiopia
Land and Water Distrubtion of Ethiopia
Natural Resources of Ethiopia
- small reserves of gold 💰
- platinum 🪙
- copper 🟧🪙
- potash 🪙
- natural gas 💨
- hydropower 💧⚡
Climate inEthiopia
tropical monsoon with wide topographic-induced variation
History of Ethiopia - a Summary
The area that is modern-day Ethiopia is rich in cultural and religious diversity with more than 80 ethnic groups. The oldest hominid yet found comes from Ethiopia, and Ethiopia was the second country to officially adopt Christianity in the 4th century A.D. A series of monarchies ruled the area that is now Ethiopia from 980 B.C. to 1855, when the Amhara kingdoms of northern Ethiopia united in an empire under Tewodros II. Many Ethiopians still speak reverently about the Battle of Adwa in 1896, when they defeated Italian forces and won their freedom from colonial rule.
Emperor Haile SELASSIE became an internationally renowned figure in 1935, when he unsuccessfully appealed to the League of Nations to prevent Italy from occupying Ethiopia from 1936 to 1941. SELASSIE survived an attempted coup in 1960, annexed modern-day Eritrea in 1962, and played a leading role in establishing the Organization of African Unity in 1963. However, in 1974, a military junta called the Derg deposed him and established a socialist state. Torn by bloody coups, uprisings, drought, and massive displacement, the Derg regime was toppled in 1991 by a coalition of opposing forces, the Ethiopian People's Revolutionary Democratic Front (EPRDF). The EPRDF became an ethno-federalist political coalition that ruled Ethiopia from 1991 until its dissolution in 2019. Ethiopia adopted its constitution in 1994 and held its first multiparty elections in 1995.
A two-and-a-half-year border war with Eritrea in the late 1990s ended with a peace treaty in 2000. Ethiopia subsequently rejected the 2007 Eritrea-Ethiopia Boundary Commission demarcation. This resulted in more than a decade of a tense “no peace, no war” stalemate between the two countries. In 2012, longtime Prime Minister MELES Zenawi died in office and was replaced by his Deputy Prime Minister HAILEMARIAM Desalegn, marking the first peaceful transition of power in decades. Following a wave of popular dissent and anti-government protest that began in 2015, HAILEMARIAM resigned in 2018, and ABIY Ahmed Ali took office the same year as Ethiopia's first ethnic Oromo prime minister. In 2018, ABIY promoted a rapprochement between Ethiopia and Eritrea that was marked with a peace agreement and a reopening of their shared border. In 2019, Ethiopia's nearly 30-year ethnic-based ruling coalition, the EPRDF, merged into a single unity party called the Prosperity Party; however, the lead coalition party, the Tigray People’s Liberation Front (TPLF), declined to join. In 2020, a military conflict erupted between forces aligned with the TPLF and the Ethiopian military. The conflict -- which was marked by atrocities committed by all parties -- ended in 2022 with a cessation of hostilities agreement between the TPLF and the Ethiopian Government. However, Ethiopia continues to experience ethnic-based violence as other groups -- including the Oromo Liberation Army (OLA) and Amhara militia Fano -- seek concessions from the Ethiopian Government.
