Faroe Islands Country Profile
Key Facts of Faroe Islands
| Government type: | parliamentary democracy (Faroese Parliament); part of the Kingdom of Denmark |
| Capital: | Torshavn |
| Languages: | Faroese 93.8% (derived from Old Norse), Danish 3.2%, other 3% (2011 est.) |
Faroe Islands Demographic Data
Ethnic Groups in Faroe Islands(2024 est.)
Religious Groups in Faroe Islands (2011 est.)
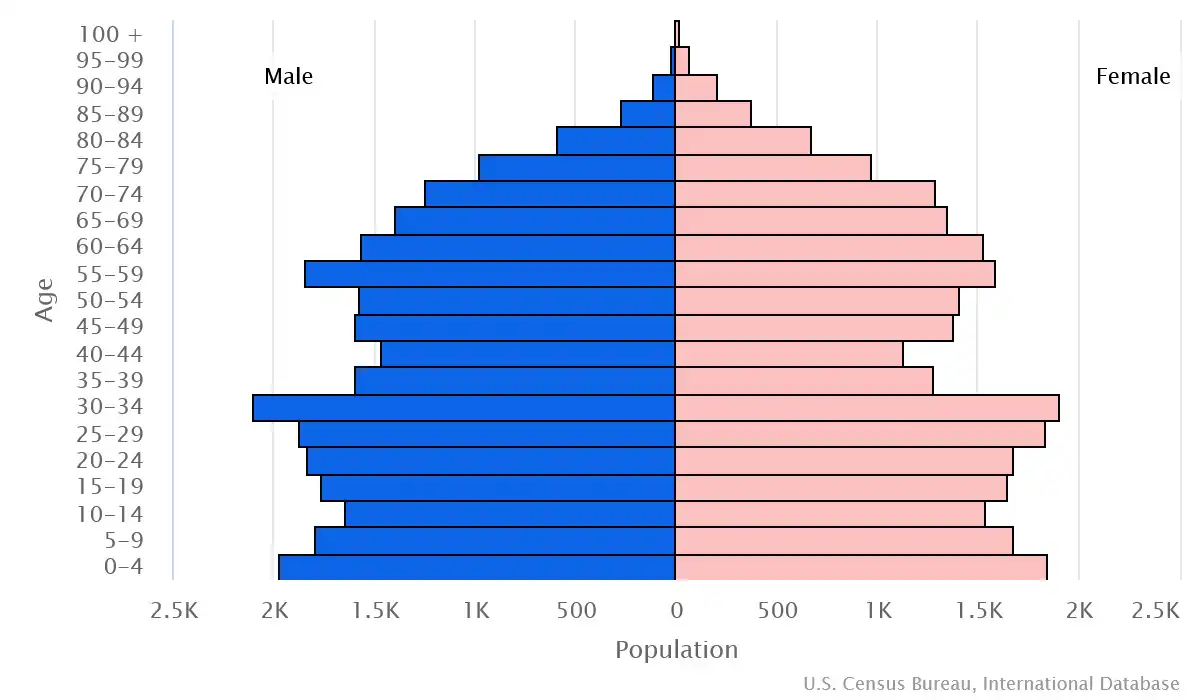
Age pyramid of Faroe Islands
Faroe Islands Economy Statistics
Economic overview of Faroe Islands
high-income Danish territorial economy; party neither to the EU nor the Schengen Area; associate Nordic Council member; very low unemployment; unique foreign ownership allowance in fishing industry; known salmon exporter; growing IT industries
Faroe Islands Real GDP (purchasing power parity) in Billion $
Faroe Islands Real GDP per capita in $
Faroe Islands's Exports & Imports in billion $
Top 5 Import Partnerin 2017 (69%) of Faroe Islands
Top 5 Import Commodities in 2017 of Faroe Islands
- goods for household consumption 🏠🍽️
- machinery and transport equipment 🚗⚙️
- fuels ⛽
- raw materials and semi-manufactures 🪙⚙️
- cars 🚗
Top 5 Export Partnerin 2017 (40%) of Faroe Islands
Top 5 Export Commodities in 2017 of Faroe Islands
- fish and fish products 🐟
Geography of Faroe Islands
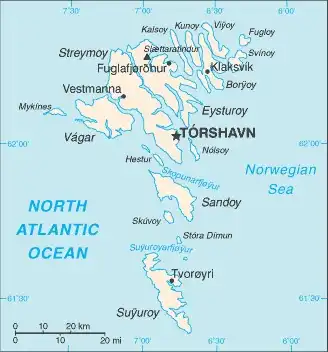
Map of Faroe Islands
Land and Water Distrubtion of Faroe Islands
Natural Resources of Faroe Islands
- fish 🐟
- whales 🐋
- hydropower 💧⚡
- possible oil and gas 🛢️
Climate inFaroe Islands
mild winters, cool summers; usually overcast; foggy, windy
History of Faroe Islands - a Summary
The Faroe Islands were already populated by about A.D. 500, but whether the original settlers were Celtic or early Norse (or someone else) has yet to be determined. Viking settlers arrived on the islands in the 9th century, and the islands served as an important stepping stone for medieval Viking exploration of the North Atlantic. The islands have been connected politically to Denmark since the 14th century, and today the Faroe Islands are a self-governing dependency of Denmark. The Home Rule Act of 1948 granted a high degree of self-government to the Faroese, who have autonomy over most internal affairs and external trade, while Denmark is responsible for justice, defense, and some foreign affairs. The Faroe Islands are not part of the European Union.
