
Germany Country Profile
Key Facts of Germany
| Government type: | federal parliamentary republic |
| Capital: | Berlin |
| Languages: | German (official); note - Danish, Frisian, Sorbian, and Romani are official minority languages; Low German, Danish, North Frisian, Sater Frisian, Lower Sorbian, Upper Sorbian, and Romani are recognized as regional languages |
Germany Demographic Data
Ethnic Groups in Germany(2022 est.)
Religious Groups in Germany (2022 est.)
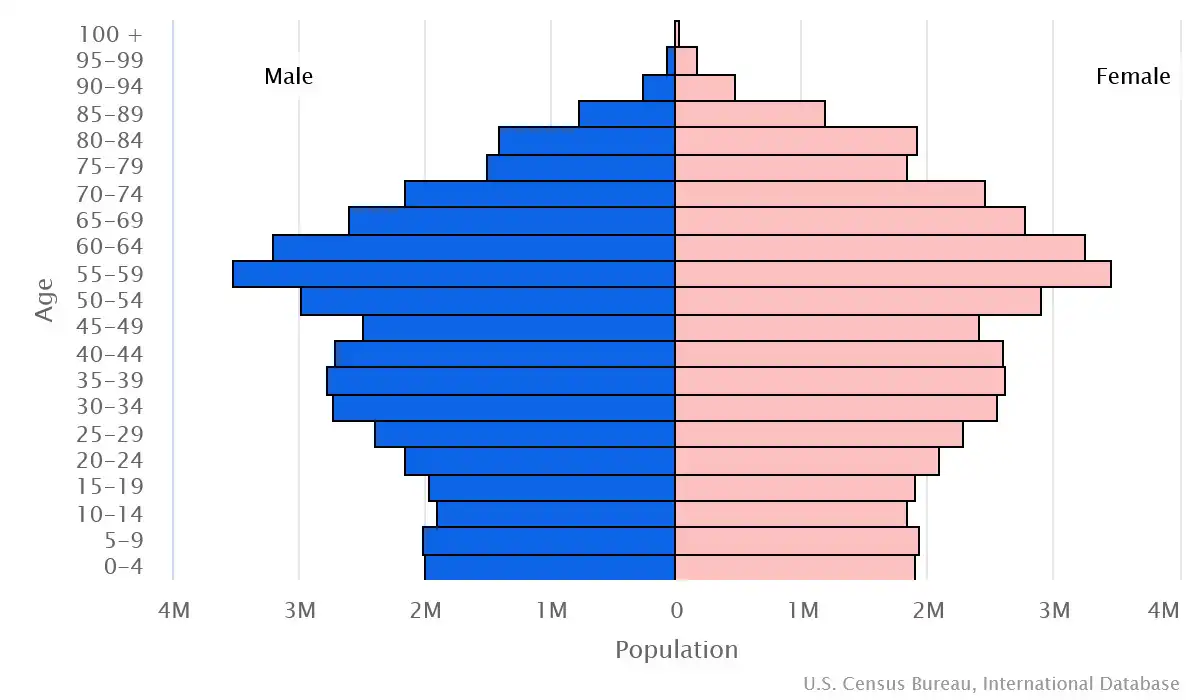
Age pyramid of Germany
Germany Economy Statistics
Economic overview of Germany
leading export-driven, core EU and eurozone economy; key automotive, chemical, engineering, finance, and green energy industries; growth stalled by energy crisis and declining exports; tight labor market with falling working-age population; fiscal rebalancing with phaseout of energy price supports
Germany Real GDP (purchasing power parity) in Billion $
Germany Real GDP per capita in $
Germany's Exports & Imports in trillion $
Top 5 Import Partnerin 2022 (36%) of Germany
Top 5 Import Commodities in 2022 of Germany
- natural gas 💨
- cars 🚗
- garments 👕
- vehicle parts/accessories 🛠️🚗
- crude petroleum 🛢️
Top 5 Export Partnerin 2022 (37%) of Germany
Top 5 Export Commodities in 2022 of Germany
- cars 🚗
- packaged medicine 💊
- vehicle parts/accessories 🛠️🚗
- vaccines 💉
- plastic products ♻️
Geography of Germany
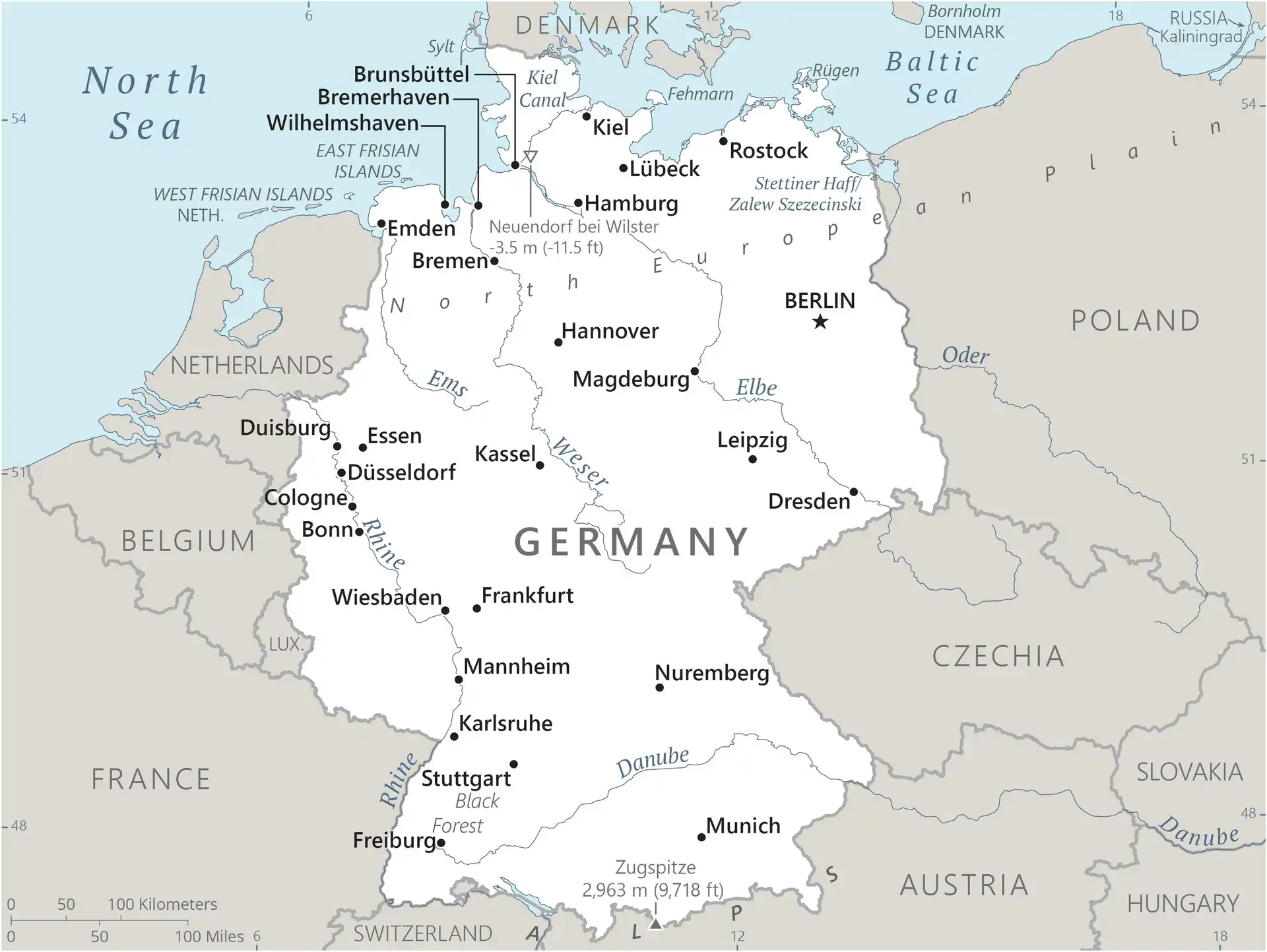
Map of Germany
Land and Water Distrubtion of Germany
Natural Resources of Germany
- coal ⚫
- lignite 🪨
- natural gas 💨
- iron ore ⛓️
- copper 🟧🪙
- nickel 🪙
- uranium ☢️
- potash 🪙
- salt 🧂
- construction materials 🏗️
- timber 🌲
- arable land 🌱
Climate inGermany
temperate and marine; cool, cloudy, wet winters and summers; occasional warm mountain (foehn) wind
History of Germany - a Summary
As Europe's largest economy and second most-populous nation (after Russia), Germany is a key member of the continent's economic, political, and defense organizations. European power struggles immersed Germany in two devastating world wars in the first half of the 20th century and left the country occupied by the victorious Allied powers of the US, UK, France, and the Soviet Union in 1945. With the advent of the Cold War, two German states were formed in 1949: the western Federal Republic of Germany (FRG) and the eastern German Democratic Republic (GDR). The democratic FRG embedded itself in key western economic and security organizations, including the EC (now the EU) and NATO, while the communist GDR was on the front line of the Soviet-led Warsaw Pact. The decline of the Soviet Union and the end of the Cold War allowed German reunification to occur in 1990. Since then, Germany has expended considerable funds to bring eastern productivity and wages up to western standards. In January 1999, Germany and 10 other EU countries introduced a common European exchange currency, the euro.
