
Greece Country Profile
Key Facts of Greece
| Government type: | parliamentary republic |
| Capital: | Athens |
| Languages: | Greek (official) 99%, other (includes English and French) 1% |
Greece Demographic Data
Ethnic Groups in Greece(2011 est.)
Religious Groups in Greece (2015 est.)
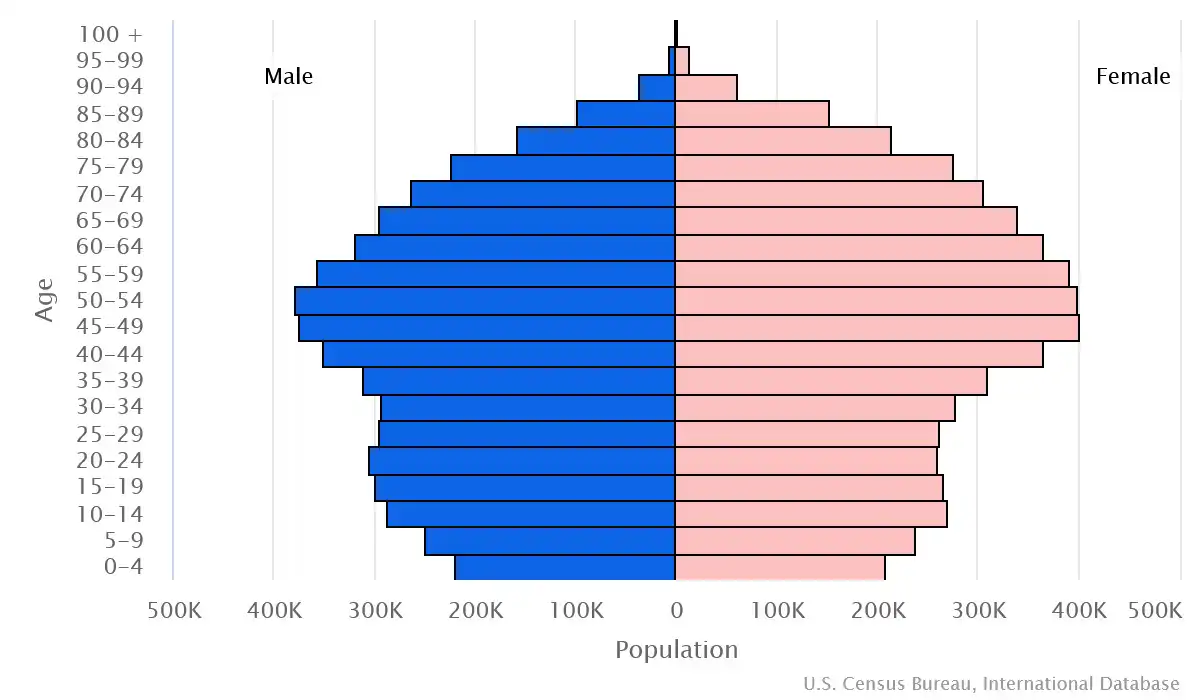
Age pyramid of Greece
Greece Economy Statistics
Economic overview of Greece
developed EU and eurozone economy; strong post-COVID growth driven by tourism, shipping industry, exports, and foreign investment supported by EU cohesion funds; public debt remains high despite recent budget surplus; challenges from negative household savings, high unemployment, corruption, and competitiveness gaps
Greece Real GDP (purchasing power parity) in Billion $
Greece Real GDP per capita in $
Greece's Exports & Imports in billion $
Top 5 Import Partnerin 2022 (44%) of Greece
Top 5 Import Commodities in 2022 of Greece
- crude petroleum 🛢️
- natural gas 💨
- refined petroleum ⛽
- garments 👕
- packaged medicine 💊
Top 5 Export Partnerin 2022 (33%) of Greece
Top 5 Export Commodities in 2022 of Greece
- refined petroleum ⛽
- packaged medicine 💊
- aluminum 🪙
- natural gas 💨
- plastic products ♻️
Geography of Greece
Map of Greece
Land and Water Distrubtion of Greece
Natural Resources of Greece
- lignite 🪨
- petroleum 🛢️
- iron ore ⛓️
- bauxite 🪨
- lead 🪙
- zinc 🔩
- nickel 🪙
- magnesite 🏔️
- marble 🪨
- salt 🧂
- hydropower potential 💧⚡
Climate inGreece
temperate; mild, wet winters; hot, dry summers
History of Greece - a Summary
Greece won independence from the Ottoman Empire in 1830 and became a kingdom. During the second half of the 19th century and the first half of the 20th century, it gradually added neighboring islands and territories, most with Greek-speaking populations. In World War II, Greece was first invaded by Italy (1940) and subsequently occupied by Germany (1941-44); fighting endured in a protracted civil war between supporters of the king and other anti-communist and communist rebels. The communists were defeated in 1949, and Greece joined NATO in 1952. In 1967, a military coup forced the king to flee the country. The ensuing military dictatorship collapsed in 1974, and Greece abolished the monarchy to become a parliamentary republic.
In 1981, Greece joined the EC (now the EU); it became the 12th member of the European Economic and Monetary Union in 2001. From 2009 until 2019, Greece suffered a severe economic crisis due to nearly a decade of chronic overspending and structural rigidities. Beginning in 2010, Greece entered three bailout agreements -- the first two with the European Commission, the European Central Bank, and the IMF; and the third in 2015 with the European Stability Mechanism -- worth in total about $300 billion. The Greek Government formally exited the third bailout in 2018, and Greece's economy has since improved significantly. In 2022, the country finalized its early repayment to the IMF and graduated on schedule from the EU's enhanced surveillance framework.
