
Indonesia Country Profile
Key Facts of Indonesia
| Government type: | presidential republic |
| Capital: | Jakarta; note - Indonesian lawmakers on 18 January 2022 approved the relocation of the country’s capital from Jakarta to a site on the island of Borneo between Samarinda City and the port city of Balikpapan; Nusantara ("archipelago"), the name of the new capital, was in development as of late 2024 and is expected to be completed in 2045 |
| Languages: | Bahasa Indonesia (official, modified form of Malay), English, Dutch, local dialects (of which the most widely spoken is Javanese); note - more than 700 languages are used in Indonesia |
Indonesia Demographic Data
Ethnic Groups in Indonesia(2010 est.)
Religious Groups in Indonesia (2022 est.)
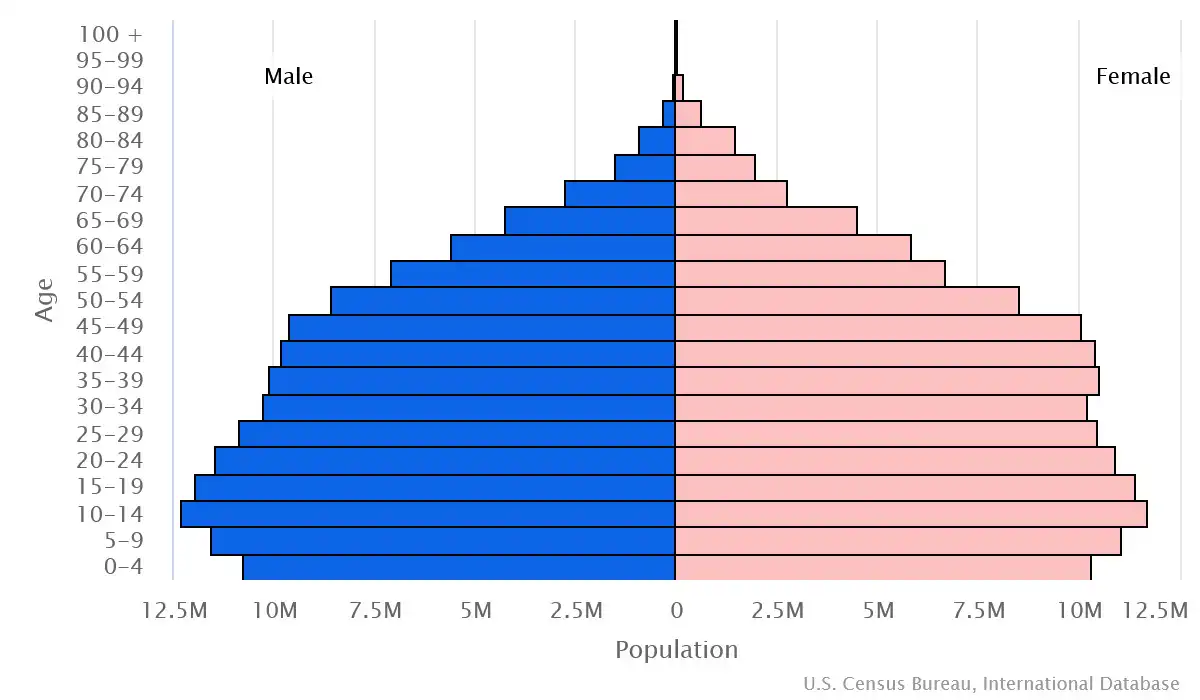
Age pyramid of Indonesia
Indonesia Economy Statistics
Economic overview of Indonesia
upper middle-income, largest and growing Southeast Asian economy; higher lending rates to moderate inflation; ongoing relocation of capital fueling infrastructure projects; major tourism sector prompting green economy goals
Indonesia Real GDP (purchasing power parity) in Billion $
Indonesia Real GDP per capita in $
Indonesia's Exports & Imports in billion $
Top 5 Import Partnerin 2022 (57%) of Indonesia
Top 5 Import Commodities in 2022 of Indonesia
- refined petroleum ⛽
- crude petroleum 🛢️
- vehicle parts/accessories 🛠️🚗
- natural gas 💨
- plastics 🧴
Top 5 Export Partnerin 2022 (52%) of Indonesia
Top 5 Export Commodities in 2022 of Indonesia
- coal ⚫
- palm oil 🛢️
- iron alloys 🪓
- natural gas 💨
- steel 🛠️
Geography of Indonesia
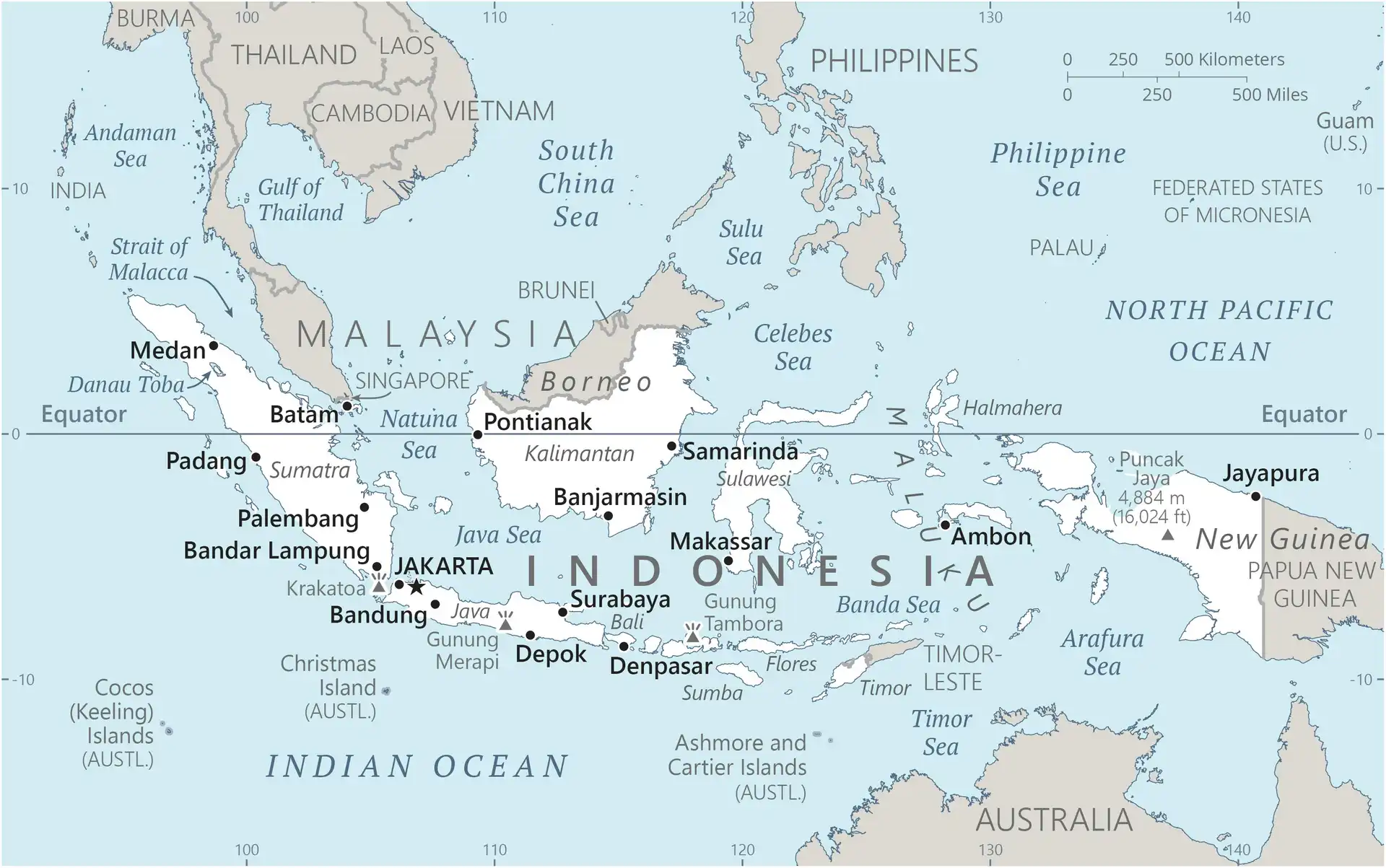
Map of Indonesia
Land and Water Distrubtion of Indonesia
Natural Resources of Indonesia
- petroleum 🛢️
- tin 🪙
- natural gas 💨
- nickel 🪙
- timber 🌲
- bauxite 🪨
- copper 🟧🪙
- fertile soils 🛢️
- coal ⚫
- gold 💰
- silver 🪙
Climate inIndonesia
tropical; hot, humid; more moderate in highlands
History of Indonesia - a Summary
The archipelago was once largely under the control of Buddhist and Hindu rulers. By around the 7th century, a Buddhist kingdom arose on Sumatra and expanded into Java and the Malay Peninsula until it was conquered in the late 13th century by the Hindu Majapahit Empire from Java. Majapahit (1290-1527) united most of modern-day Indonesia and Malaysia. Traders introduced Islam around the 11th century, and the religion was gradually over the next 500 years. The Portuguese conquered parts of Indonesia in the 16th century, but the Dutch ousted them (except in East Timor) and began colonizing the islands in the early 17th century. It would be the early 20th century before Dutch colonial rule was established across the entirety of what would become the boundaries of the modern Indonesian state.
Japan occupied the islands from 1942 to 1945. Indonesia declared its independence shortly before Japan's surrender, but it required four years of sometimes brutal fighting, intermittent negotiations, and UN mediation before the Netherlands agreed to transfer sovereignty in 1949. A period of sometimes unruly parliamentary democracy ended in 1957 when President SOEKARNO declared martial law and instituted "Guided Democracy." After an abortive coup in 1965 by alleged communist sympathizers, SOEKARNO was gradually eased from power. From 1967 until 1998, President SUHARTO ruled Indonesia with his "New Order" government. After street protests toppled SUHARTO in 1998, free and fair legislative elections took place in 1999 while the country's first direct presidential election occurred in 2004. Indonesia has since become a robust democracy, holding four direct presidential elections, each considered by international observers to have been largely free and fair.
Indonesia is now the world's third-most-populous democracy and the world's largest Muslim-majority nation. It has had strong economic growth since overcoming the Asian financial crisis of the late 1990s. By the 2020s, it had the largest economy in Southeast Asia, and its economy ranked in the world's top 10 in terms of purchasing power parity. It has also made considerable gains in reducing poverty. Although relations amongst its diverse population--there are more than 300 ethnic groups--have been harmonious in the 2000s, there have been areas of sectarian discontent and violence, as well as instances of religious extremism and terrorism. A political settlement to an armed separatist conflict in Aceh was achieved in 2005, but a separatist group in Papua continued to conduct a low-intensity conflict as of 2024.
