Japan Country Profile
Key Facts of Japan
| Government type: | parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
| Capital: | Tokyo |
| Languages: | Japanese |
Japan Demographic Data
Ethnic Groups in Japan(2022 est.)
Religious Groups in Japan (2021 est.)
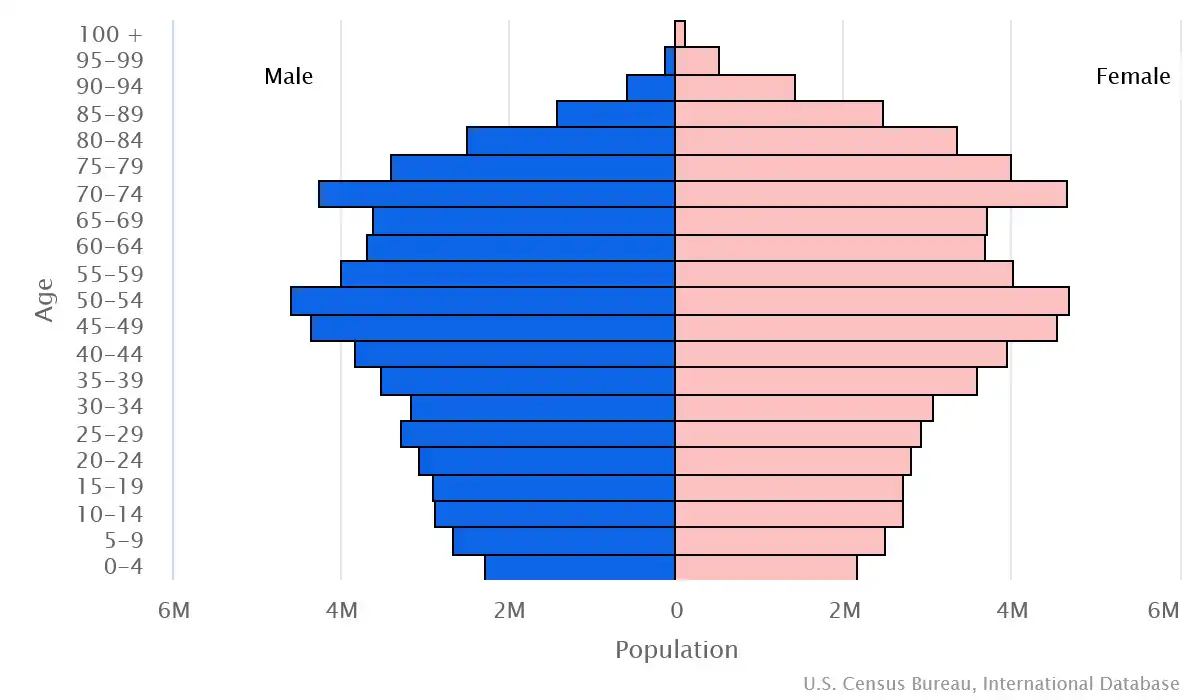
Age pyramid of Japan
Japan Economy Statistics
Economic overview of Japan
second-largest East Asian economy; trade-oriented and highly diversified; high public debt levels; following years of near-zero interest rates, gradual increases to address inflation and depreciation of yen; strong rebound in tourism; aging population poses challenges to labor force participation
Japan Real GDP (purchasing power parity) in Billion $
Japan Real GDP per capita in $
Japan's Exports & Imports in billion $
Top 5 Import Partnerin 2022 (51%) of Japan
Top 5 Import Commodities in 2022 of Japan
- crude petroleum 🛢️
- natural gas 💨
- coal ⚫
- integrated circuits 💻
- garments 👕
Top 5 Export Partnerin 2022 (56%) of Japan
Top 5 Export Commodities in 2022 of Japan
- cars 🚗
- machinery ⚙️
- integrated circuits 💻
- vehicle parts/accessories 🛠️🚗
- refined petroleum ⛽
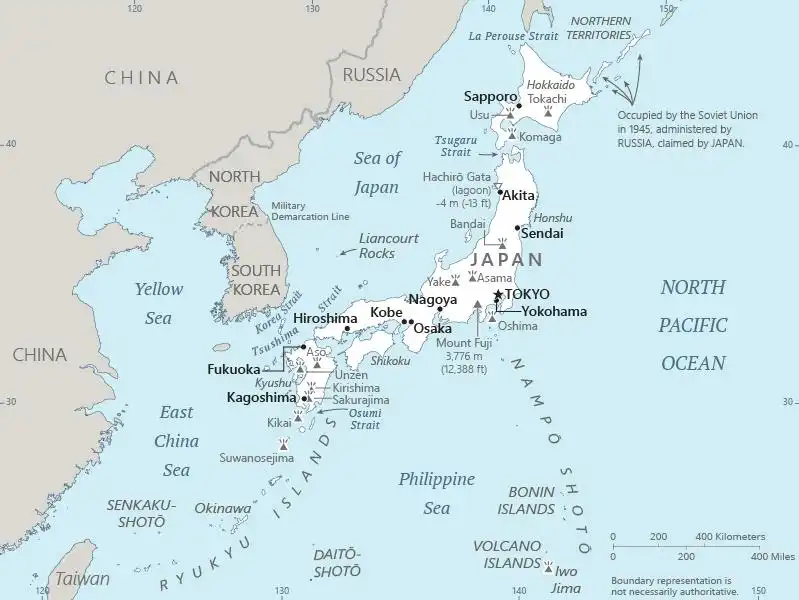
Geography of Japan
Map of Japan
Land and Water Distrubtion of Japan
Natural Resources of Japan
- negligible mineral resources ⚪
- fish 🐟
Climate inJapan
varies from tropical in south to cool temperate in north
History of Japan - a Summary
In 1603, after decades of civil warfare, the Tokugawa shogunate (a military-led, dynastic government) ushered in a long period of relative political stability and isolation from foreign influence. For more than two centuries, this policy enabled Japan to enjoy a flowering of its indigenous culture. Japan opened its ports after signing the Treaty of Kanagawa with the US in 1854 and began to intensively modernize and industrialize. During the late 19th and early 20th centuries, Japan became a regional power that was able to defeat the forces of both China and Russia. It occupied Korea, Formosa (Taiwan), and southern Sakhalin Island. In 1931-32, Japan occupied Manchuria, and in 1937, it launched a full-scale invasion of China. Japan attacked US forces at Pearl Harbor, Hawaii, in 1941, triggering America's entry into World War II, and Japan soon occupied much of East and Southeast Asia. After its defeat in World War II, the country recovered to become an economic power and a US ally.
While the emperor retains his throne as a symbol of national unity, elected politicians hold the decision-making power. After three decades of unprecedented growth, Japan's economy experienced a major slowdown starting in the 1990s, but the country remains an economic power. In 2011, Japan's strongest-ever earthquake and an accompanying tsunami devastated the northeast part of Honshu, killed thousands, and damaged several nuclear power plants. ABE Shinzo was reelected as prime minister in 2012, and he embarked on ambitious economic and security reforms to improve Japan's economy and bolster the country's international standing. In 2019, ABE became Japan's longest-serving post-war prime minister; he resigned in 2020 and was succeeded by SUGA Yoshihide. KISHIDA Fumio became prime minister in 2021.
