
Latvia Country Profile
Key Facts of Latvia
| Government type: | parliamentary republic |
| Capital: | Riga |
| Languages: | Latvian (official) 56.3%, Russian 33.8%, other 0.6% (includes Polish, Ukrainian, and Belarusian), unspecified 9.4% (2011 est.) |
Latvia Demographic Data
Ethnic Groups in Latvia(2021 est.)
Religious Groups in Latvia (2017 est.)
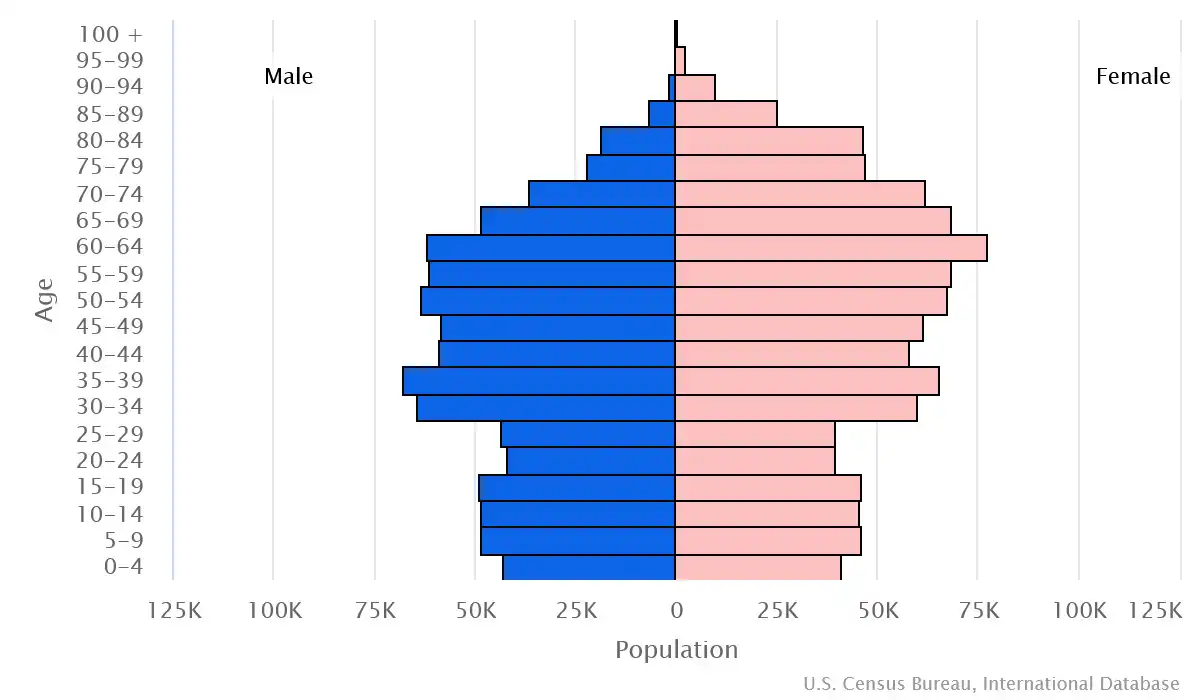
Age pyramid of Latvia
Latvia Economy Statistics
Economic overview of Latvia
high-income EU and eurozone member; economic contraction triggered by export decline and energy shocks; recovery driven by easing inflation, wage growth, and investments supported by EU funds; challenges from skilled labor shortages, capital market access, large informal sector, and green and digital transitions
Latvia Real GDP (purchasing power parity) in Billion $
Latvia Real GDP per capita in $
Latvia's Exports & Imports in billion $
Top 5 Import Partnerin 2022 (56%) of Latvia
Top 5 Import Commodities in 2022 of Latvia
- natural gas 💨
- refined petroleum ⛽
- electricity ⚡
- cars 🚗
- packaged medicine 💊
Top 5 Export Partnerin 2022 (45%) of Latvia
Top 5 Export Commodities in 2022 of Latvia
- wood 🌲
- wheat 🌾
- natural gas 💨
- electricity ⚡
- broadcasting equipment 📡
Geography of Latvia
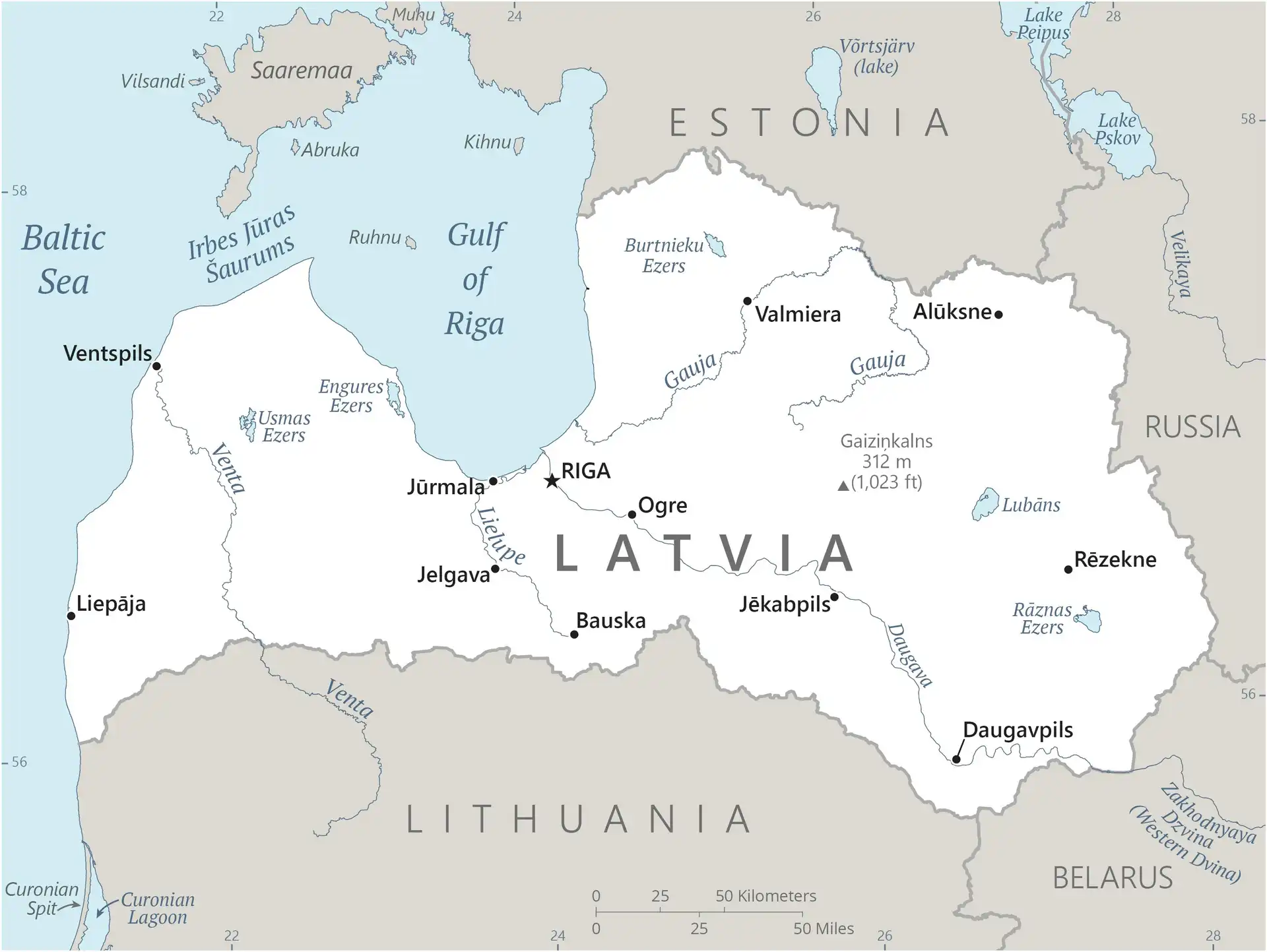
Map of Latvia
Land and Water Distrubtion of Latvia
Natural Resources of Latvia
- peat 🪵
- limestone 🪨
- dolomite 🪨
- amber 🟧
- hydropower 💧⚡
- timber 🌲
- arable land 🌱
Climate inLatvia
maritime; wet, moderate winters
History of Latvia - a Summary
Several eastern Baltic tribes merged in medieval times to form the ethnic core of the Latvian people (ca. 8th-12th centuries A.D.). The region subsequently came under the control of Germans, Poles, Swedes, and finally Russians. A Latvian republic emerged following World War I, but the USSR annexed it in 1940 -- an action never recognized by the US and many other countries. Latvia reestablished its independence in 1991 after the breakup of the Soviet Union. Although the last Russian troops left in 1994, the status of the Russian minority (some 25% of the population) remains of concern to Moscow. Latvia joined both NATO and the EU in 2004; it joined the euro zone in 2014 and the OECD in 2016.
