
Lebanon Country Profile
Key Facts of Lebanon
| Government type: | parliamentary democratic republic |
| Capital: | Beirut |
| Languages: | Arabic (official), French, English, Armenian |
Lebanon Demographic Data
Ethnic Groups in Lebanon
Religious Groups in Lebanon (2020 est.)
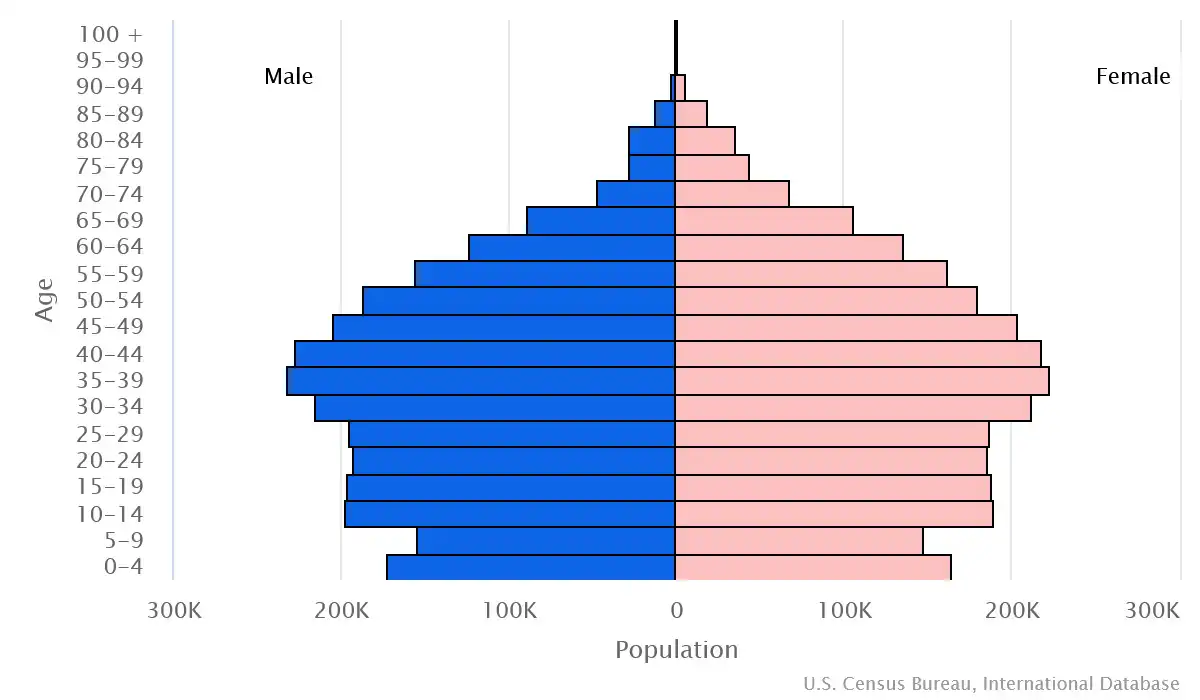
Age pyramid of Lebanon
Lebanon Economy Statistics
Economic overview of Lebanon
lower middle-income Middle Eastern economy; hyperinflation and sharp poverty increases; banks have ceased lending; economic contraction, destroyed infrastructure, and reduced consumer demand resulting from Israel-Hezbollah conflict
Lebanon Real GDP (purchasing power parity) in Billion $
Lebanon Real GDP per capita in $
Lebanon's Exports & Imports in billion $
Top 5 Import Partnerin 2022 (48%) of Lebanon
Top 5 Import Commodities in 2022 of Lebanon
- refined petroleum ⛽
- cars 🚗
- gold 💰
- broadcasting equipment 📡
- diamonds 💎
Top 5 Export Partnerin 2022 (44%) of Lebanon
Top 5 Export Commodities in 2022 of Lebanon
- diamonds 💎
- plastics 🧴
- jewelry 💍
- gold 💰
- scrap iron 🛠️
Geography of Lebanon
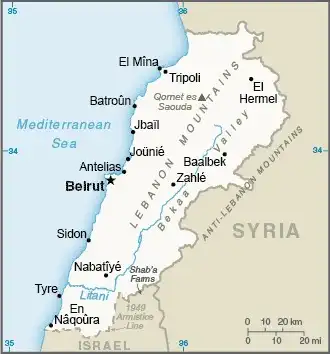
Map of Lebanon
Land and Water Distrubtion of Lebanon
Natural Resources of Lebanon
- limestone 🪨
- iron ore ⛓️
- salt 🧂
- water-surplus state in a water-deficit region 💧
- arable land 🌱
Climate inLebanon
Mediterranean; mild to cool, wet winters with hot, dry summers; the Lebanon Mountains experience heavy winter snows
History of Lebanon - a Summary
As a result of its location at the crossroads of three continents, the area that is modern-day Lebanon is rich in cultural and religious diversity. This region was subject to various foreign conquerors for much of its history, including the Romans, Arabs, and Ottomans. Following World War I, France acquired a mandate over the northern portion of the former Ottoman Empire province of Syria. From it the French demarcated the region of Lebanon in 1920, and it gained independence in 1943. Lebanon subsequently experienced periods of political turmoil interspersed with prosperity built on its position as a regional center for finance and trade.
The country's 1975-90 civil war, which resulted in an estimated 120,000 fatalities, was followed by years of social and political instability, and sectarianism remains a key element of Lebanese political life. The Israeli defense forces, which occupied parts of Lebanon during the civil war, did not completely withdraw until 2000. Neighboring Syria influenced Lebanon's foreign and domestic policies while its military occupied Lebanon from 1976 until 2005, but its influence diminished significantly after 2005. Over 1.5 million Syrian refugees fled to Lebanon after the start of the Syrian conflict in 2011. Hizballah -- a major Lebanese political party, militia, and US-designated foreign terrorist organization -- and Israel continued attacks and counterattacks against each other after Syria's withdrawal and fought a brief war in 2006. After HAMAS attacked Israel on 7 October 2023, the intensity and frequency of these cross-border attacks increased substantially into a cycle of hostilities, mostly limited to the border areas as of January 2024. Lebanon's borders with Syria and Israel remain unresolved.
Lebanon's prosperity has significantly diminished since the beginning of the country's economic crisis in 2019, which has crippled its economy, shut down its previously lucrative banking sector, reduced the value of its currency, and caused many Lebanese to emigrate in search of better prospects.
