
Liechtenstein Country Profile
Key Facts of Liechtenstein
| Government type: | constitutional monarchy |
| Capital: | Vaduz |
| Languages: | German 91.5% (official, Alemannic is the main dialect), Italian 1.5%, Turkish 1.3%, Portuguese 1.1%, other 4.6% (2015 est.) |
Liechtenstein Demographic Data
Ethnic Groups in Liechtenstein(2021 est.)
Religious Groups in Liechtenstein (2015 est.)
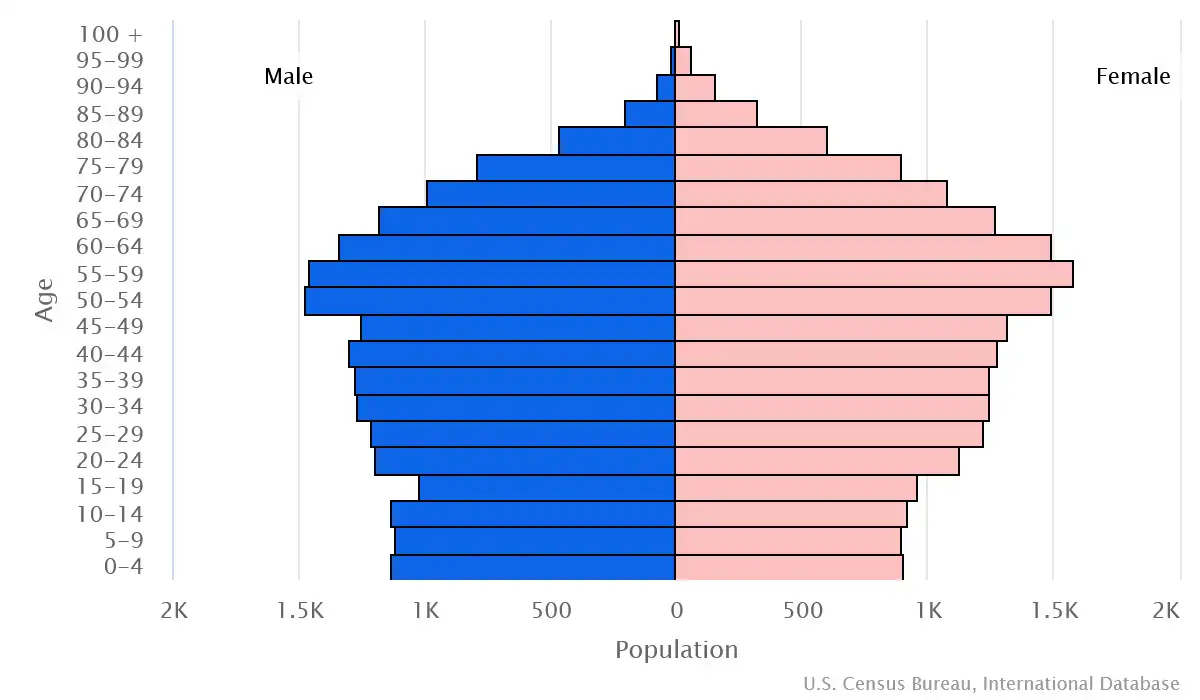
Age pyramid of Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein Economy Statistics
Economic overview of Liechtenstein
high-income European economy; Schengen Area participant; key European financial leader; integrated with Swiss economy and franc currency user; one of the highest GDP per capita countries; relies on US and Eurozone markets for exports
Liechtenstein Real GDP (purchasing power parity) in Billion $
Liechtenstein Real GDP per capita in $
No data
Liechtenstein's Exports & Imports in billion $
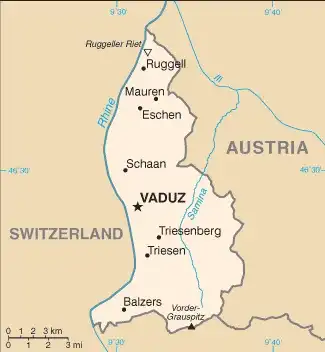
Geography of Liechtenstein
Map of Liechtenstein
Land and Water Distrubtion of Liechtenstein
Natural Resources of Liechtenstein
- hydroelectric potential ⚡
- arable land 🌱
Climate inLiechtenstein
continental; cold, cloudy winters with frequent snow or rain; cool to moderately warm, cloudy, humid summers
History of Liechtenstein - a Summary
The Principality of Liechtenstein was established within the Holy Roman Empire in 1719. Occupied by both French and Russian troops during the Napoleonic Wars, it became a sovereign state in 1806 and joined the German Confederation in 1815. Liechtenstein became fully independent in 1866 when the Confederation dissolved. Until the end of World War I, it was closely tied to Austria, but the economic devastation caused by that conflict forced Liechtenstein to enter into a customs and monetary union with Switzerland. Since World War II (in which Liechtenstein remained neutral), the country's low taxes have spurred outstanding economic growth. In 2000, shortcomings in banking regulatory oversight resulted in concerns about the use of financial institutions for money laundering. However, Liechtenstein implemented anti-money laundering legislation and a Mutual Legal Assistance Treaty with the US that went into effect in 2003.
