
Lithuania Country Profile
Key Facts of Lithuania
| Government type: | semi-presidential republic |
| Capital: | Vilnius |
| Languages: | Lithuanian (official) 85.3%, Russian 6.8%, Polish 5.1%, other 1.1%, two mother tongues 1.7% (2021 est.) |
Lithuania Demographic Data
Ethnic Groups in Lithuania(2021 est.)
Religious Groups in Lithuania (2021 est.)
Age pyramid of Lithuania

Lithuania Economy Statistics
Economic overview of Lithuania
high-income EU and eurozone member, largest Baltic economy; growth stalled due to Ukraine war impact on energy, exports, and fiscal spending for defense and refugee support; rebound supported by EU fund-driven investments and reduced inflation; structural challenges include pension reform, labor market inefficiencies, health care, and education spending
Lithuania Real GDP (purchasing power parity) in Billion $
Lithuania Real GDP per capita in $
Lithuania's Exports & Imports in billion $
Top 5 Import Partnerin 2022 (42%) of Lithuania
Top 5 Import Commodities in 2022 of Lithuania
- crude petroleum 🛢️
- natural gas 💨
- electricity ⚡
- cars 🚗
- plastic products ♻️
Top 5 Export Partnerin 2022 (41%) of Lithuania
Top 5 Export Commodities in 2022 of Lithuania
- refined petroleum ⛽
- furniture 🛋️
- plastic products ♻️
- natural gas 💨
- wheat 🌾
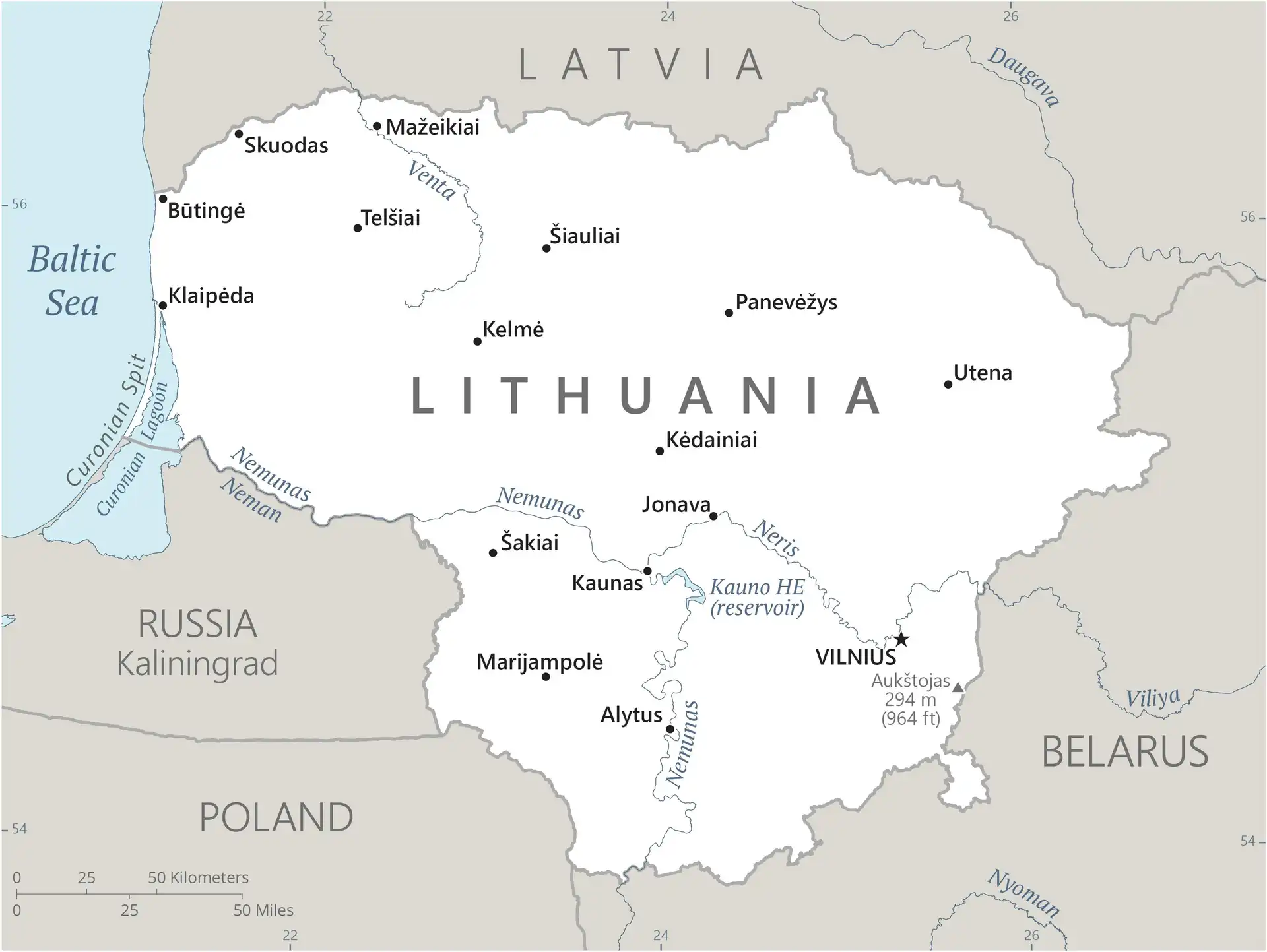
Geography of Lithuania
Map of Lithuania
Land and Water Distrubtion of Lithuania
Natural Resources of Lithuania
- peat 🪵
- arable land 🌱
- amber 🟧
Climate inLithuania
transitional, between maritime and continental; wet, moderate winters and summers
History of Lithuania - a Summary
Lithuanian lands were united under MINDAUGAS in 1236; over the next century, Lithuania extended its territory through alliances and conquest to include most of present-day Belarus and Ukraine. By the end of the 14th century, Lithuania was the largest state in Europe. An alliance with Poland in 1386 led the two countries into a union through a common ruler. In 1569, Lithuania and Poland formally united into a single dual state, the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. This entity survived until 1795 when surrounding countries partitioned its remnants. Lithuania regained its independence after World War I, but the USSR annexed it in 1940 -- an action never recognized by the US and many other countries. In 1990, Lithuania became the first of the Soviet republics to declare its independence, but Moscow did not recognize this proclamation until 1991. The last Russian troops withdrew in 1993. Lithuania subsequently restructured its economy for integration into West European institutions; it joined both NATO and the EU in 2004. In 2015, Lithuania joined the euro zone, and it joined the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development in 2018.
