
Luxembourg Country Profile
Key Facts of Luxembourg
| Government type: | constitutional monarchy |
| Capital: | Luxembourg |
| Languages: | Luxembourgish (official administrative, judicial, and national language) 48.9%, Portuguese 15.4%, French (official administrative, judicial, and legislative language) 14.9%, Italian 3.6%, English 3.6%, German (official administrative and judicial language) 2.9%, other 10.8% (2021 est.) |
Luxembourg Demographic Data
Ethnic Groups in Luxembourg(2022 est.)
Religious Groups in Luxembourg (2020 est.)
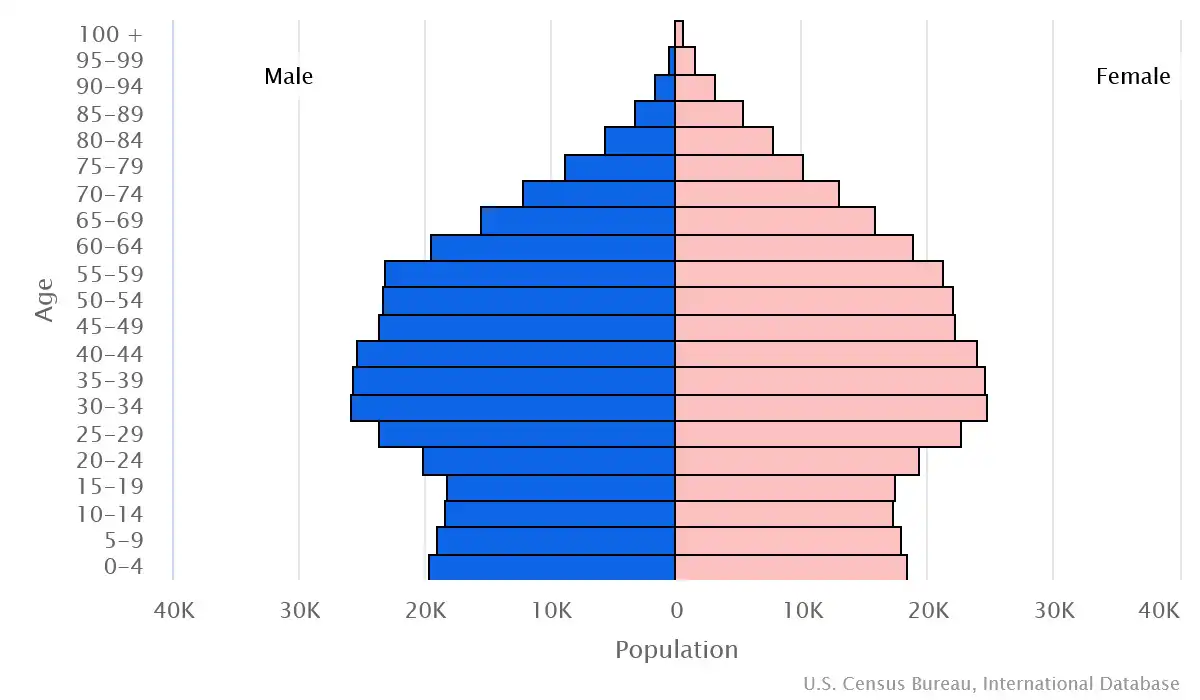
Age pyramid of Luxembourg
Luxembourg Economy Statistics
Economic overview of Luxembourg
high-income EU and eurozone economy; global, highly capitalized banking sector; one of highest GDP-per-capita countries; trending toward recovery after economic contraction from energy-driven inflation, reduced exports and investments, and financial sector weakness
Luxembourg Real GDP (purchasing power parity) in Billion $
Luxembourg Real GDP per capita in $
Luxembourg's Exports & Imports in billion $
Top 5 Import Partnerin 2022 (72%) of Luxembourg
Top 5 Import Commodities in 2022 of Luxembourg
- refined petroleum ⛽
- cars 🚗
- electricity ⚡
- natural gas 💨
- scrap iron 🛠️
Top 5 Export Partnerin 2022 (57%) of Luxembourg
Top 5 Export Commodities in 2022 of Luxembourg
- iron blocks 🧱
- plastic products ♻️
- rubber tires 🧤
- plastics 🧴
- gas turbines 🌀
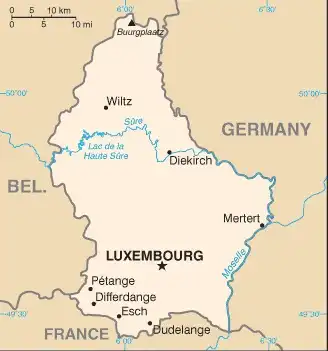
Geography of Luxembourg
Map of Luxembourg
Land and Water Distrubtion of Luxembourg
Natural Resources of Luxembourg
- iron ore (no longer exploited) ⛓️
- arable land 🌱
Climate inLuxembourg
modified continental with mild winters, cool summers
History of Luxembourg - a Summary
Founded in 963, Luxembourg became a grand duchy in 1815 and a constituent part of the Kingdom of the Netherlands after the Congress of Vienna. When Belgium declared independence from the Netherlands in 1839, Luxembourg lost more than half of its territory to Belgium but gained a larger measure of autonomy within the Kingdom of the Netherlands. Luxembourg gained full independence in 1867 by promising to remain permanently neutral. Overrun by Germany in both world wars, its neutrality ended in 1948 when it entered into the Benelux Customs Union and joined NATO the following year. In 1957, Luxembourg became one of the six founding countries of the EEC (later the EU), and in 1999 it joined the euro currency zone.
