
Montenegro Country Profile
Key Facts of Montenegro
| Government type: | parliamentary republic |
| Capital: | Podgorica; note - Cetinje retains the status of "Old Royal Capital" |
| Languages: | Serbian 42.9%, Montenegrin (official) 37%, Bosnian 5.3%, Albanian 5.3%, Serbo-Croat 2%, other 3.5%, unspecified 4% (2011 est.) |
Montenegro Demographic Data
Ethnic Groups in Montenegro(2011 est.)
Religious Groups in Montenegro (2011 est.)
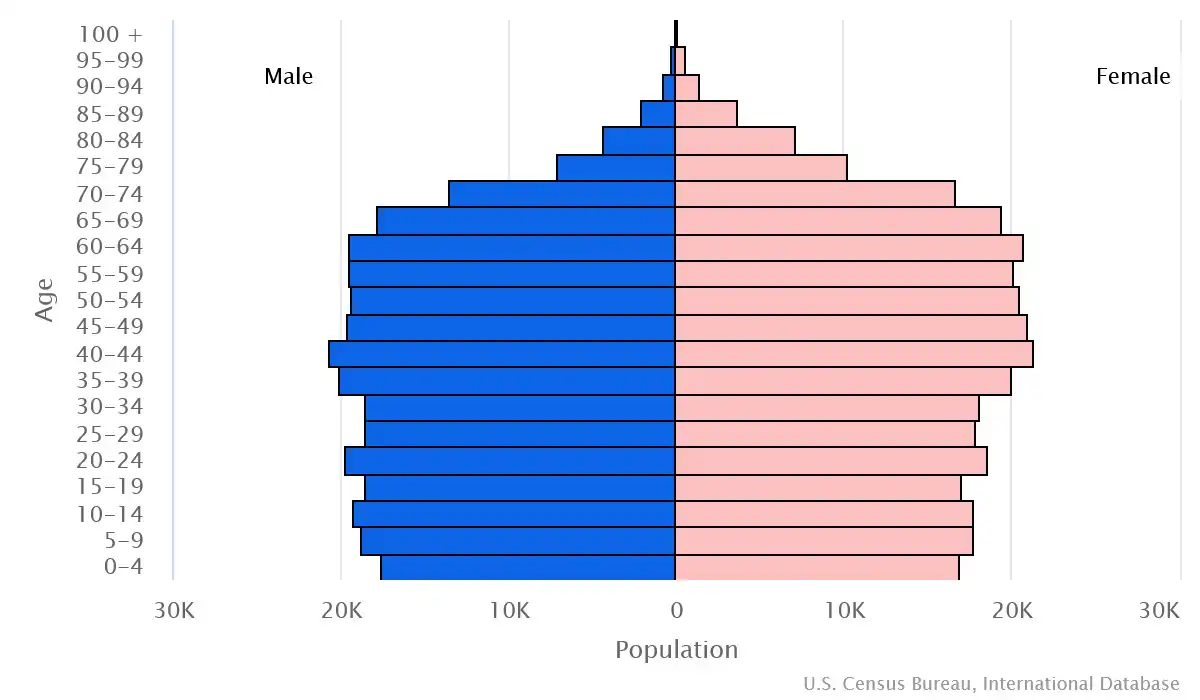
Age pyramid of Montenegro
Montenegro Economy Statistics
Economic overview of Montenegro
upper middle-income, small Balkan economy; uses euro as de facto currency; strong growth driven by tourism and consumption; new impetus for EU accession under Europe Now government; influx of affluent migrants from Russia and Ukraine; progress in fiscal position subject to risks from pension costs, debt service, and informal sector
Montenegro Real GDP (purchasing power parity) in Billion $
Montenegro Real GDP per capita in $
Montenegro's Exports & Imports in billion $
Top 5 Import Partnerin 2022 (54%) of Montenegro
Top 5 Import Commodities in 2022 of Montenegro
- electricity ⚡
- refined petroleum ⛽
- aluminum 🪙
- cars 🚗
- garments 👕
Top 5 Export Partnerin 2022 (61%) of Montenegro
Top 5 Export Commodities in 2022 of Montenegro
- copper ore 🟧🪙
- electricity ⚡
- aluminum 🪙
- aluminum ore 🪙
- packaged medicine 💊
Geography of Montenegro
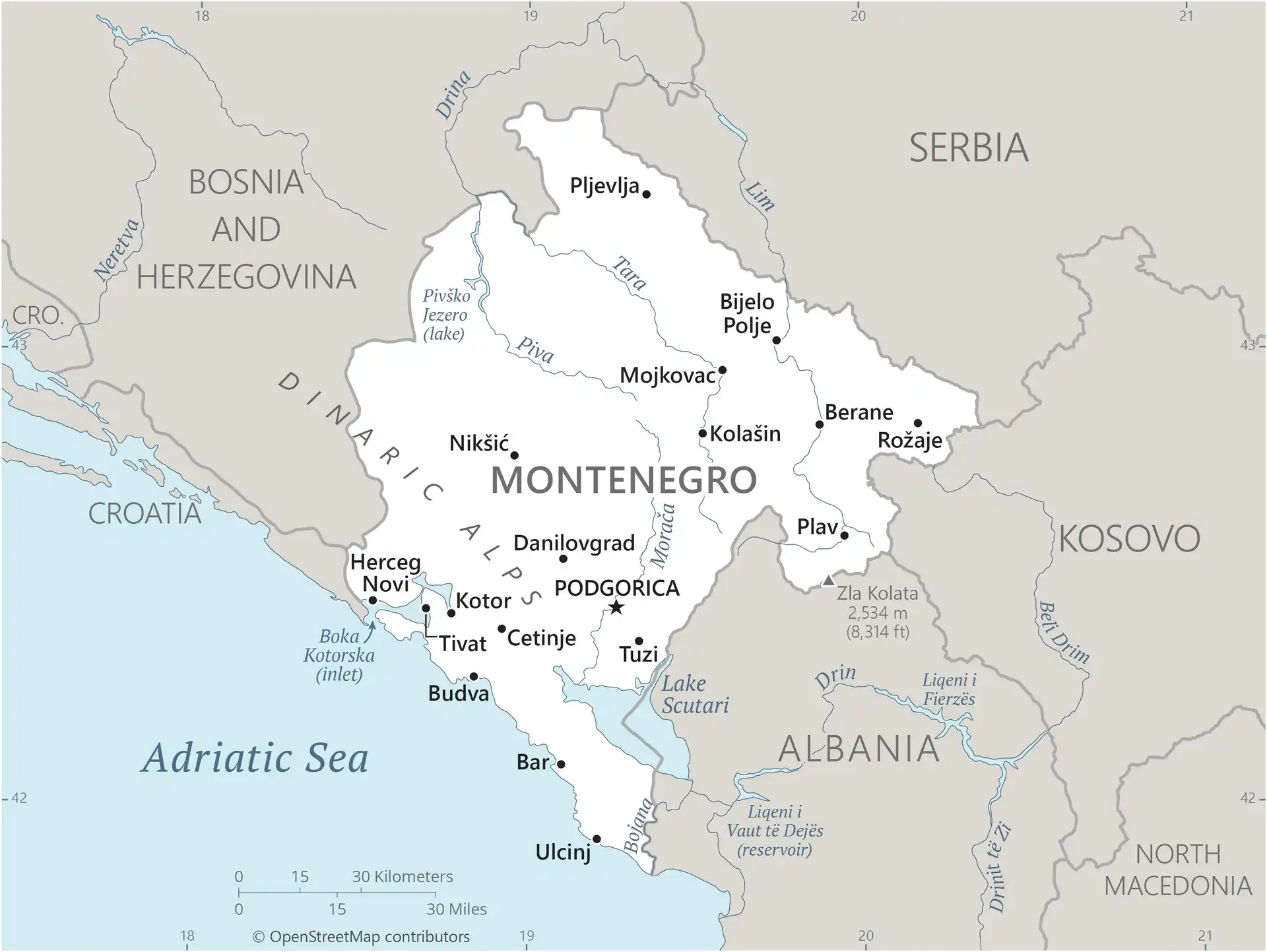
Map of Montenegro
Land and Water Distrubtion of Montenegro
Natural Resources of Montenegro
- bauxite 🪨
- hydroelectricity ⚡
Climate inMontenegro
Mediterranean climate, hot dry summers and autumns and relatively cold winters with heavy snowfalls inland
History of Montenegro - a Summary
The use of the name Crna Gora or Black Mountain (Montenegro) began in the 13th century in reference to a highland region in the Serbian province of Zeta. Under Ottoman control beginning in 1496, Montenegro was a semi-autonomous theocracy ruled by a series of bishop princes until 1852, when it became a secular principality. Montenegro fought a series of wars with the Ottomans and eventually won recognition as an independent sovereign principality at the Congress of Berlin in 1878. In 1918, the country was absorbed by the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes, which became the Kingdom of Yugoslavia in 1929. At the end of World War II, Montenegro joined the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (SFRY). When the SFRY dissolved in 1992, Montenegro and Serbia created the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (FRY), which shifted in 2003 to a looser State Union of Serbia and Montenegro. Montenegro voted to restore its independence on 3 June 2006. Montenegro became an official EU candidate in 2010 and joined NATO in 2017.
