Morocco Country Profile
Key Facts of Morocco

| Government type: | parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
| Capital: | Rabat |
| Languages: | Arabic (official), Tamazight languages (Tamazight (official), Tachelhit, Tarifit), French (often the language of business, government, and diplomacy) |
Morocco Demographic Data
Ethnic Groups in Morocco
Religious Groups in Morocco (2020 est.)
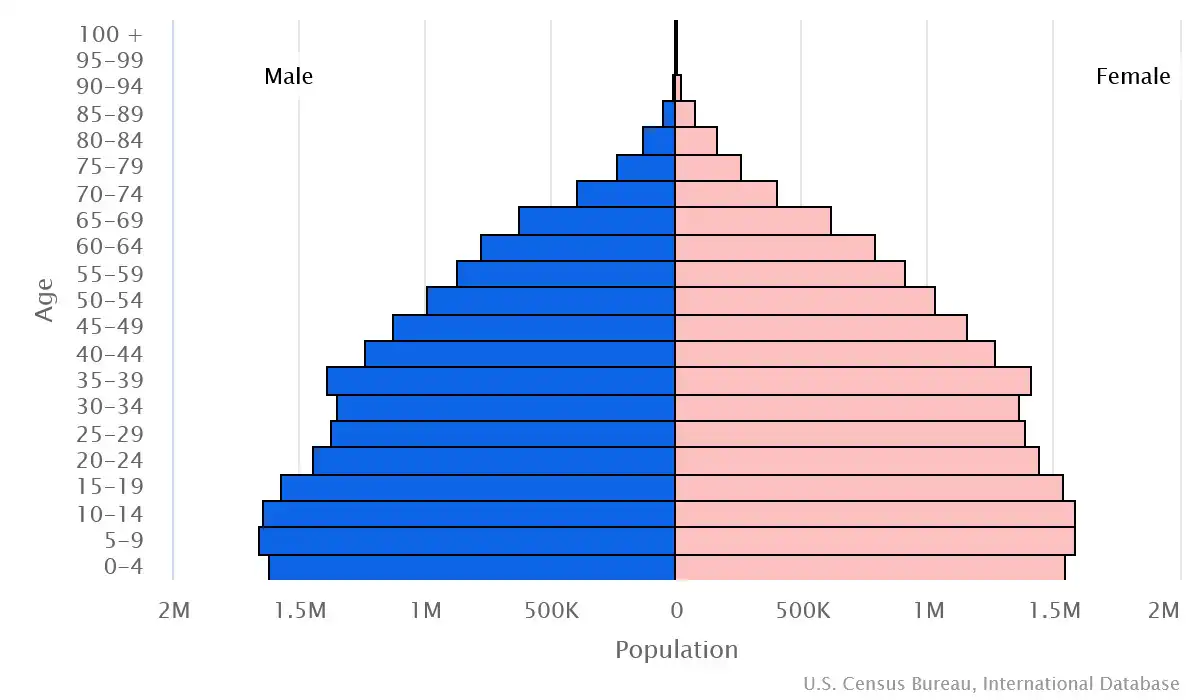
Age pyramid of Morocco
Morocco Economy Statistics
Economic overview of Morocco
lower middle-income North African economy; ongoing recovery from recent drought and earthquake; rebounding via tourism, manufacturing, and raw materials processing; significant trade and investment with EU; reform programs include fiscal rebalancing, state enterprise governance and private sector investments
Morocco Real GDP (purchasing power parity) in Billion $
Morocco Real GDP per capita in $
Morocco's Exports & Imports in billion $
Top 5 Import Partnerin 2022 (50%) of Morocco
Top 5 Import Commodities in 2022 of Morocco
- refined petroleum ⛽
- wheat 🌾
- natural gas 💨
- coal ⚫
- vehicle parts/accessories 🛠️🚗
Top 5 Export Partnerin 2022 (50%) of Morocco
Top 5 Export Commodities in 2022 of Morocco
- fertilizers 💩
- cars 🚗
- garments 👕
- insulated wire 🔌
- phosphoric acid 🧴
Geography of Morocco
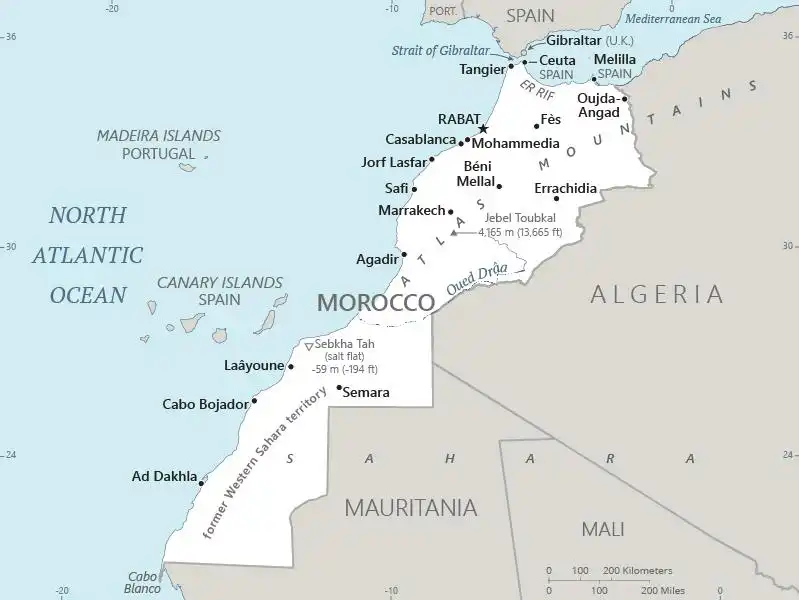
Map of Morocco
Land and Water Distrubtion of Morocco
Natural Resources of Morocco
- phosphates ⛏️
- iron ore ⛓️
- manganese 🪙
- lead 🪙
- zinc 🔩
- fish 🐟
- salt 🧂
Climate inMorocco
Mediterranean in the north, becoming more extreme in the interior; in the south, hot, dry desert; rain is rare; cold offshore air currents produce fog and heavy dew
History of Morocco - a Summary
In 788, about a century after the Arab conquest of North Africa, a series of Muslim dynasties began to rule in Morocco. In the 16th century, the Sa'adi monarchy, particularly under Ahmad al-MANSUR (1578-1603), repelled foreign invaders and inaugurated a golden age. The Alaouite Dynasty, to which the current Moroccan royal family belongs, dates from the 17th century. In 1860, Spain occupied northern Morocco and ushered in a half-century of trade rivalry among European powers that saw Morocco's sovereignty steadily erode; in 1912, the French imposed a protectorate over the country. A protracted independence struggle with France ended successfully in 1956. The internationalized city of Tangier and most Spanish possessions were turned over to the new country that same year. Sultan MOHAMMED V, the current monarch's grandfather, organized the new state as a constitutional monarchy and in 1957 assumed the title of king.
Since Spain's 1976 withdrawal from Western Sahara, Morocco has extended its de facto administrative control to roughly 75% of this territory; however, the UN does not recognize Morocco as the administering power for Western Sahara. The UN since 1991 has monitored a cease-fire, which broke down in late 2020, between Morocco and the Polisario Front -- an organization advocating the territory’s independence -- and restarted negotiations over the status of the territory in 2018. In 2020, the US recognized Morocco's sovereignty over all of Western Sahara.
In 2011, King MOHAMMED VI responded to the spread of pro-democracy protests in the North Africa region by implementing a reform program that included a new constitution, passed by popular referendum, under which some new powers were extended to parliament and the prime minister, but ultimate authority remains in the hands of the monarch. Later that year, the Justice and Development Party (PJD) -- a moderate Islamist democratic party -- won the largest number of seats in parliamentary elections, becoming the first Islamist party to lead the Moroccan Government. In 2015, Morocco held its first direct elections for regional councils, which was one of the reforms included in the 2011 constitution. The PJD again won the largest number of seats in nationwide parliamentary elections in 2016, but it lost its plurality to the probusiness National Rally of Independents (RNI) in 2021. In 2020, Morocco signed a normalization agreement with Israel, similar to those that Bahrain, the United Arab Emirates, and Sudan had concluded with Israel earlier that year.
