Namibia Country Profile
Key Facts of Namibia
| Government type: | presidential republic |
| Capital: | Windhoek |
| Languages: | Oshiwambo languages 49.7%, Nama/Damara 11%, Kavango languages 10.4%, Afrikaans 9.4%, Herero languages 9.2%, Zambezi languages 4.9%, English (official) 2.3%, other African languages 1.5%, other European languages 0.7%, other 1% (2016 est.) |
Namibia Demographic Data
Ethnic Groups in Namibia
Religious Groups in Namibia (2020 est.)
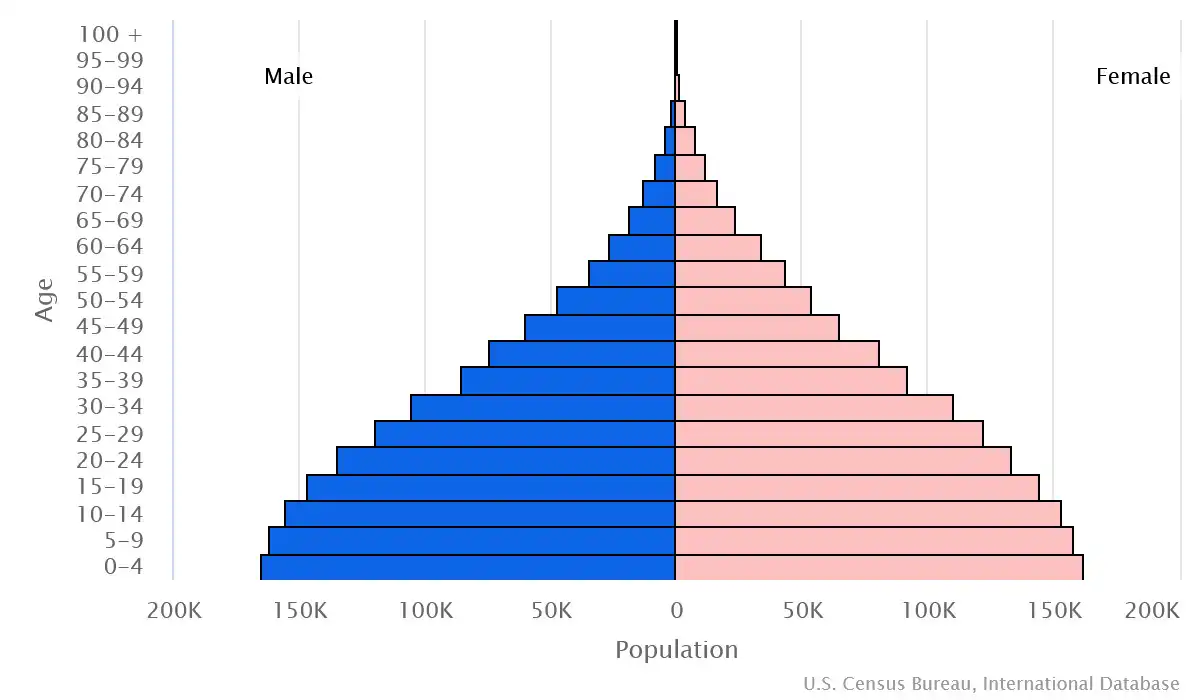
Age pyramid of Namibia
Namibia Economy Statistics
Economic overview of Namibia
upper middle-income, export-driven Sub-Saharan economy; natural resource rich; Walvis Bay port expansion for trade; high potential for renewable power generation and energy independence; major nature-based tourist locale; natural resource rich; shortage of skilled labor
Namibia Real GDP (purchasing power parity) in Billion $
Namibia Real GDP per capita in $
Namibia's Exports & Imports in billion $
Top 5 Import Partnerin 2022 (61%) of Namibia
Top 5 Import Commodities in 2022 of Namibia
- refined petroleum ⛽
- ships 🚢
- copper ore 🟧🪙
- trucks 🚚
- electricity ⚡
Top 5 Export Partnerin 2022 (58%) of Namibia
Top 5 Export Commodities in 2022 of Namibia
- diamonds 💎
- gold 💰
- fish 🐟
- radioactive chemicals 🪨
- ships 🚢
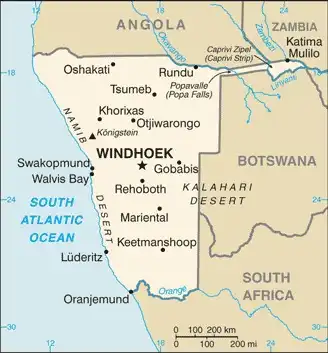
Geography of Namibia
Map of Namibia
Land and Water Distrubtion of Namibia
Natural Resources of Namibia
- diamonds 💎
- copper 🟧🪙
- uranium ☢️
- gold 💰
- silver 🪙
- lead 🪙
- tin 🪙
- lithium 🔋
- cadmium 🟩
- tungsten 🔧
- zinc 🔩
- salt 🧂
- hydropower 💧⚡
- fish 🐟
Climate inNamibia
desert; hot, dry; rainfall sparse and erratic
History of Namibia - a Summary
Various ethnic groups occupied southwestern Africa prior to Germany establishing a colony over most of the territory in 1884. South Africa occupied the colony, then known as German South West Africa, in 1915 during World War I and administered it as a mandate until after World War II, when it annexed the territory. In 1966, the Marxist South-West Africa People's Organization (SWAPO) guerrilla group launched a war of independence for the area that became Namibia, but it was not until 1988 that South Africa agreed to end its administration in accordance with a UN peace plan for the entire region. Namibia gained independence in 1990, and SWAPO has governed it since, although the party has dropped much of its Marxist ideology. President Hage GEINGOB was elected in 2014 in a landslide victory, replacing Hifikepunye POHAMBA, who stepped down after serving two terms. SWAPO retained its parliamentary super majority in the 2014 elections. In 2019 elections, GEINGOB was reelected but by a substantially reduced majority, and SWAPO narrowly lost its super majority in parliament.
