Niger Country Profile
Key Facts of Niger
| Government type: | formerly, semi-presidential republic |
| Capital: | Niamey |
| Languages: | Hausa, Zarma, French (official), Fufulde, Tamashek, Kanuri, Gurmancema, Tagdal |
Niger Demographic Data
Ethnic Groups in Niger(2006 est.)
Religious Groups in Niger (2020 est.)
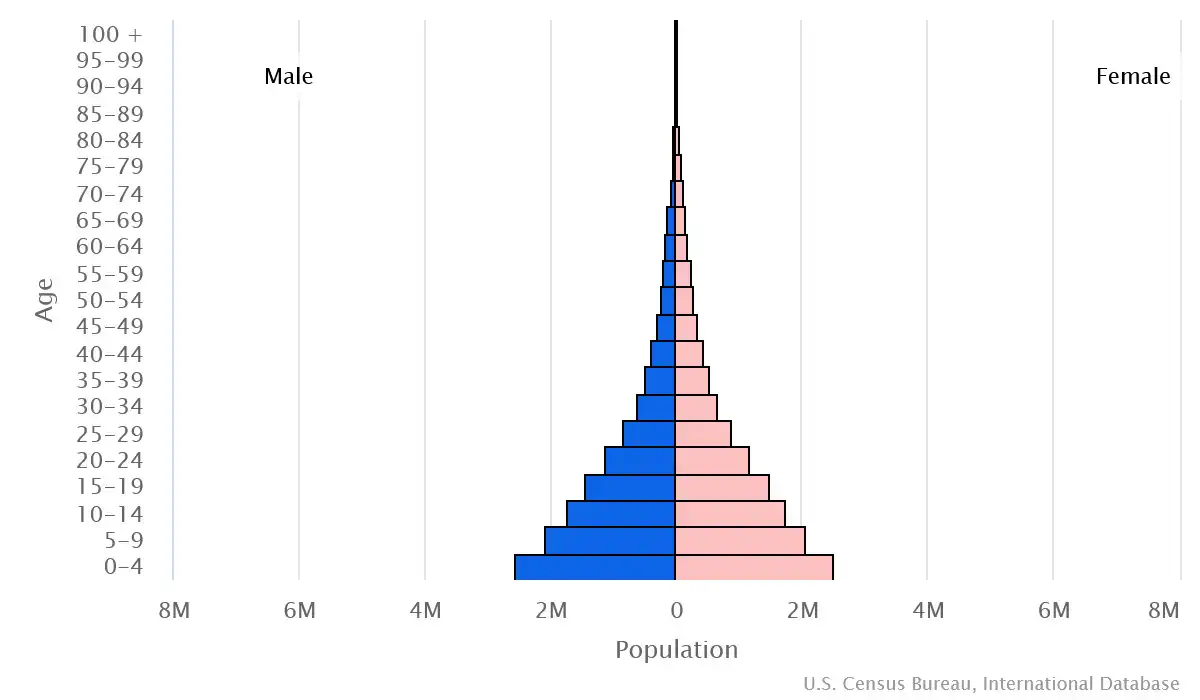
Age pyramid of Niger
Niger Economy Statistics
Economic overview of Niger
low-income Sahel economy; major instability and humanitarian crises limit economic activity; COVID-19 eliminated recent antipoverty gains; economy rebounding since December 2020 Nigerian border reopening and new investments; uranium resource rich
Niger Real GDP (purchasing power parity) in Billion $
Niger Real GDP per capita in $
Niger's Exports & Imports in billion $
Top 5 Import Partnerin 2022 (54%) of Niger
Top 5 Import Commodities in 2022 of Niger
- weapons parts and accessories ⚔️
- rice 🍚
- aircraft ✈️
- tobacco 🚬
- iron pipes 🛠️
Top 5 Export Partnerin 2022 (92%) of Niger
Top 5 Export Commodities in 2022 of Niger
- gold 💰
- oil seeds 🛢️
- radioactive chemicals 🪨
- refined petroleum ⛽
- uranium and thorium ore ☢️
Geography of Niger
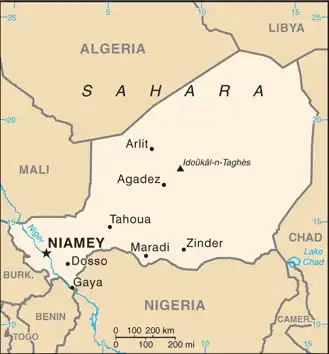
Map of Niger
Land and Water Distrubtion of Niger
Natural Resources of Niger
- uranium ☢️
- coal ⚫
- iron ore ⛓️
- tin 🪙
- phosphates ⛏️
- gold 💰
- molybdenum 🪨
- gypsum ⚪🪨
- salt 🧂
- petroleum 🛢️
Climate inNiger
desert; mostly hot, dry, dusty; tropical in extreme south
History of Niger - a Summary
Nomadic peoples from the Saharan north and agriculturalists from the south settled present-day Niger. The Taureg kingdom of Takedda was one of the largest kingdoms in the north and played a prominent role in regional trade in the 14th century. In the south, the primary ethnic groups were the Songhai-Zarma in the west, the Hausa in the center, and the Kanuri in the east. When European colonizers arrived in the 19th century, the region was an assemblage of disparate local kingdoms.
In the late 19th century, the British and French agreed to partition the middle regions of the Niger River, and France began its conquest of what would become the colony of Niger. France experienced determined local resistance -- particularly during the Tuareg uprising (1916-1917) -- but established a colonial administration in 1922.
After achieving independence from France in 1960, Niger experienced single-party or military rule until 1991, when political pressure forced General Ali SAIBOU to allow multiparty elections. Political infighting and democratic backsliding led to coups in 1996 and 1999. In 1999, military officers restored democratic rule and held elections that brought Mamadou TANDJA to power. TANDJA was reelected in 2004 and spearheaded a 2009 constitutional amendment allowing him to extend his presidential term. In 2010, military officers led another coup that deposed TANDJA. ISSOUFOU Mahamadou was elected in 2011 and reelected in 2016. In 2021, BAZOUM Mohamed won the presidential election, marking Niger’s first transition from one democratically elected president to another. Nonetheless, a military junta led by General Abdourahamane TIANI once again seized power in July 2023, detaining President BAZOUM and announcing the creation of a National Council for the Safeguarding of the Homeland (CNSP).
Niger is one of the poorest countries in the world with minimal government services and insufficient funds to develop its resource base. It is ranked fourth to last in the world on the UN Development Program's Human Development Index of 2023/2024. The largely agrarian and subsistence-based economy is frequently disrupted by extended droughts common to the Sahel region of Africa. The Nigerien Government continues its attempts to diversify the economy through increased oil production and mining projects. In addition, Niger is facing increased security concerns on its borders from various external threats including insecurity in Libya, spillover from the conflict and terrorism in Mali, and violent extremism in northeastern Nigeria.
