
Oman Country Profile
Key Facts of Oman
| Government type: | absolute monarchy |
| Capital: | Muscat |
| Languages: | Arabic (official), English, Baluchi, Swahili, Urdu, Indian dialects |
Oman Demographic Data
Ethnic Groups in Oman(est. ?)
Religious Groups in Oman (2020 est.)
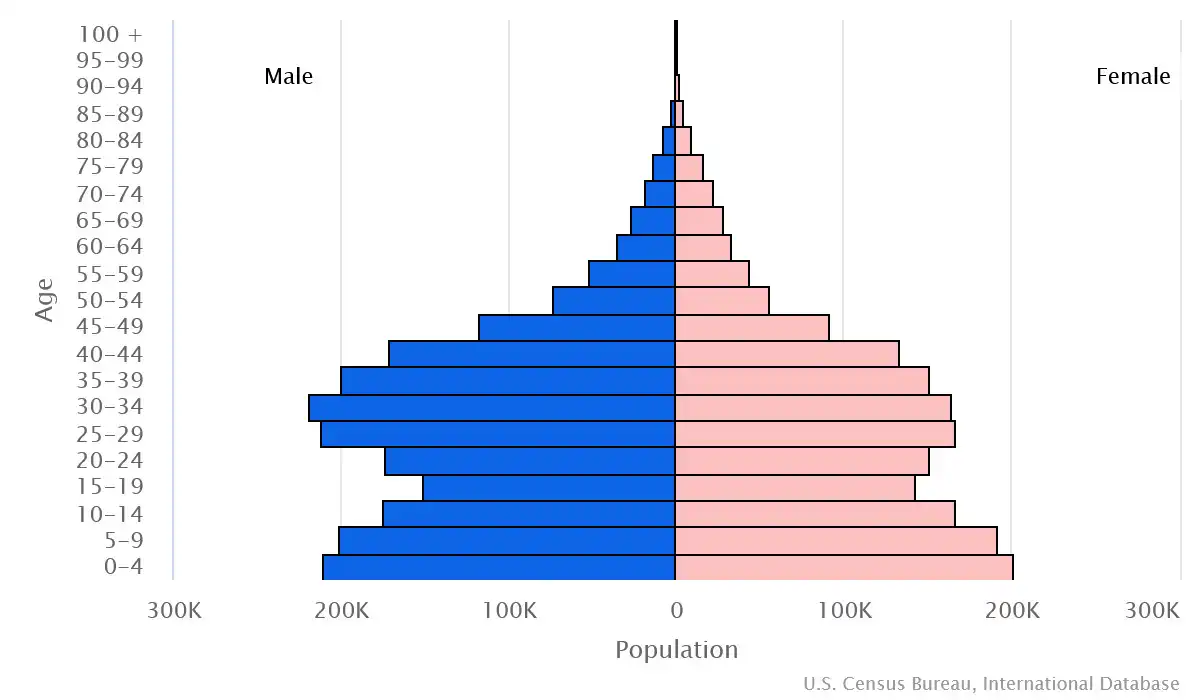
Age pyramid of Oman
Oman Economy Statistics
Economic overview of Oman
high-income, oil-based economy; large welfare system; growing government debt; citizenship-based labor force growth policy; US free trade agreement; diversifying portfolio; high female labor force participation
Oman Real GDP (purchasing power parity) in Billion $
Oman Real GDP per capita in $
Oman's Exports & Imports in billion $
Top 5 Import Partnerin 2022 (62%) of Oman
Top 5 Import Commodities in 2022 of Oman
- refined petroleum ⛽
- cars 🚗
- iron ore ⛓️
- milk 🥛
- iron pipes 🛠️
Top 5 Export Partnerin 2022 (65%) of Oman
Top 5 Export Commodities in 2022 of Oman
- crude petroleum 🛢️
- natural gas 💨
- refined petroleum ⛽
- fertilizers 💩
- semi-finished iron 🛠️
Geography of Oman
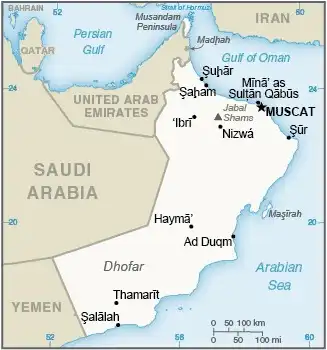
Map of Oman
Land and Water Distrubtion of Oman
Natural Resources of Oman
- petroleum 🛢️
- copper 🟧🪙
- asbestos 🏭💨
- some marble 🪨
- limestone 🪨
- chromium 🟩
- gypsum ⚪🪨
- natural gas 💨
Climate inOman
dry desert; hot, humid along coast; hot, dry interior; strong southwest summer monsoon (May to September) in far south
History of Oman - a Summary
The inhabitants of the area of present-day Oman have long prospered from Indian Ocean trade. In the late 18th century, the nascent sultanate in Muscat signed the first in a series of friendship treaties with Britain. Over time, Oman's dependence on British political and military advisors increased, although the sultanate never became a British colony. In 1970, QABOOS bin Said Al Said overthrew his father and ruled as sultan for the next five decades. His extensive modernization program opened the country to the outside world. He prioritized strategic ties to the UK and US, and his moderate, independent foreign policy allowed Oman to maintain good relations with its neighbors and avoid external entanglements.
In 2011, the popular uprisings that swept the Middle East and North Africa inspired demonstrations in Oman that called for more jobs and economic benefits and an end to corruption. In response, QABOOS implemented economic and political reforms such as granting Oman’s legislative body more power and authorizing direct elections for its lower house. Additionally, the sultan increased unemployment benefits and issued a royal directive mandating a national public- and private-sector job creation plan. As part of the government's efforts to decentralize authority and allow greater citizen participation in local governance, Oman successfully conducted its first municipal council elections in 2012. QABOOS, Oman's longest reigning monarch, died in 2020. His cousin, HAYTHAM bin Tariq Al Said, former Minister of Heritage and Culture, was sworn in as Oman's new sultan the same day.
