
Republic of Congo Country Profile
Key Facts of Republic of Congo
| Government type: | presidential republic |
| Capital: | Brazzaville |
| Languages: | French (official), French Lingala and Monokutuba (trade languages), many local languages and dialects (of which Kikongo is the most widespread) |
Republic of Congo Demographic Data
Ethnic Groups in Republic of Congo(2014-15 est.)
Religious Groups in Republic of Congo (2007 est.)
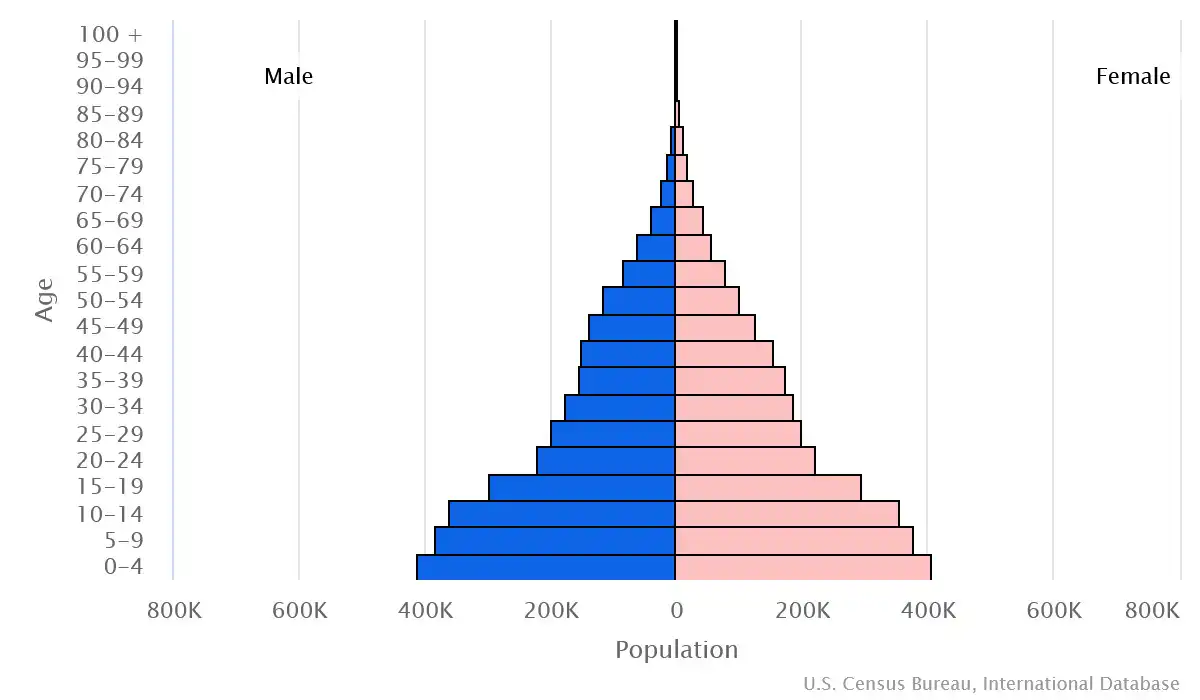
Age pyramid of Republic of Congo
Republic of Congo Economy Statistics
Economic overview of Republic of Congo
primarily an oil- and natural resources-based economy; recovery from mid-2010s oil devaluation has been slow and curtailed by COVID-19; extreme poverty increasing, particularly in southern rural regions; attempting to implement recommended CEMAC reforms; increasing likelihood of debt default
Republic of Congo Real GDP (purchasing power parity) in Billion $
Republic of Congo Real GDP per capita in $
Republic of Congo's Exports & Imports in billion $
Top 5 Import Partnerin 2022 (52%) of Republic of Congo
Top 5 Import Commodities in 2022 of Republic of Congo
- poultry 🍗
- garments 👕
- vaccines 💉
- ships 🚢
- fish 🐟
Top 5 Export Partnerin 2022 (83%) of Republic of Congo
Top 5 Export Commodities in 2022 of Republic of Congo
- crude petroleum 🛢️
- refined copper 🟧🪙
- wood 🌲
- tin ores 🪙
- rare earth ores 🪙
Geography of Republic of Congo
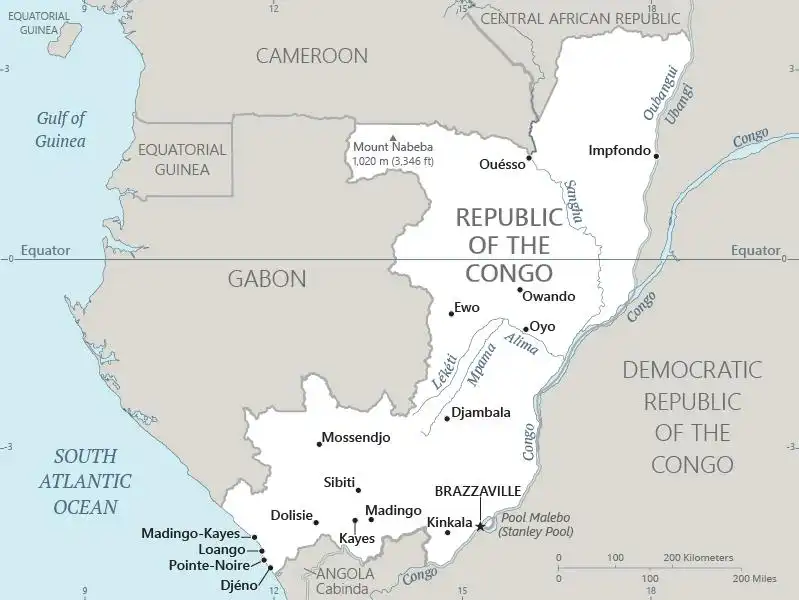
Map of Republic of Congo
Land and Water Distrubtion of Republic of Congo
Natural Resources of Republic of Congo
- petroleum 🛢️
- timber 🌲
- potash 🪙
- lead 🪙
- zinc 🔩
- uranium ☢️
- copper 🟧🪙
- phosphates ⛏️
- gold 💰
- magnesium 🔋
- natural gas 💨
- hydropower 💧⚡
Climate inRepublic of Congo
tropical; rainy season (March to June); dry season (June to October); persistent high temperatures and humidity; particularly enervating climate astride the Equator
History of Republic of Congo - a Summary
Upon independence in 1960, the former French region of Middle Congo became the Republic of the Congo. From 1968 to 1992, the country was named the People’s Republic of the Congo. A quarter-century of experimentation with Marxism was abandoned in 1990, and a democratically elected government took office in 1992, at which time the country reverted to "the Republic of the Congo" name. A two-year civil war that ended in 1999 restored to power former President Denis SASSOU-Nguesso, who had ruled from 1979 to 1992. A new constitution adopted three years later provided for a multi-party system and a seven-year presidential term, and the next elections retained SASSOU-Nguesso. After a year of renewed fighting, SASSOU-Nguesso and southern-based rebel groups agreed to a final peace accord in 2003. SASSOU-Nguesso was reelected in 2009 and, after passing a constitutional referendum allowing him to run for additional terms, was reelected again in 2016 and 2021. The Republic of the Congo is one of Africa's largest petroleum producers.
