
Singapore Country Profile
Key Facts of Singapore
| Government type: | parliamentary republic |
| Capital: | Singapore |
| Languages: | English (official) 48.3%, Mandarin (official) 29.9%, other Chinese dialects (includes Hokkien, Cantonese, Teochew, Hakka) 8.7%, Malay (official) 9.2%, Tamil (official) 2.5%, other 1.4% (2020 est.) |
Singapore Demographic Data
Ethnic Groups in Singapore(2021 est.)
Religious Groups in Singapore (2020 est.)
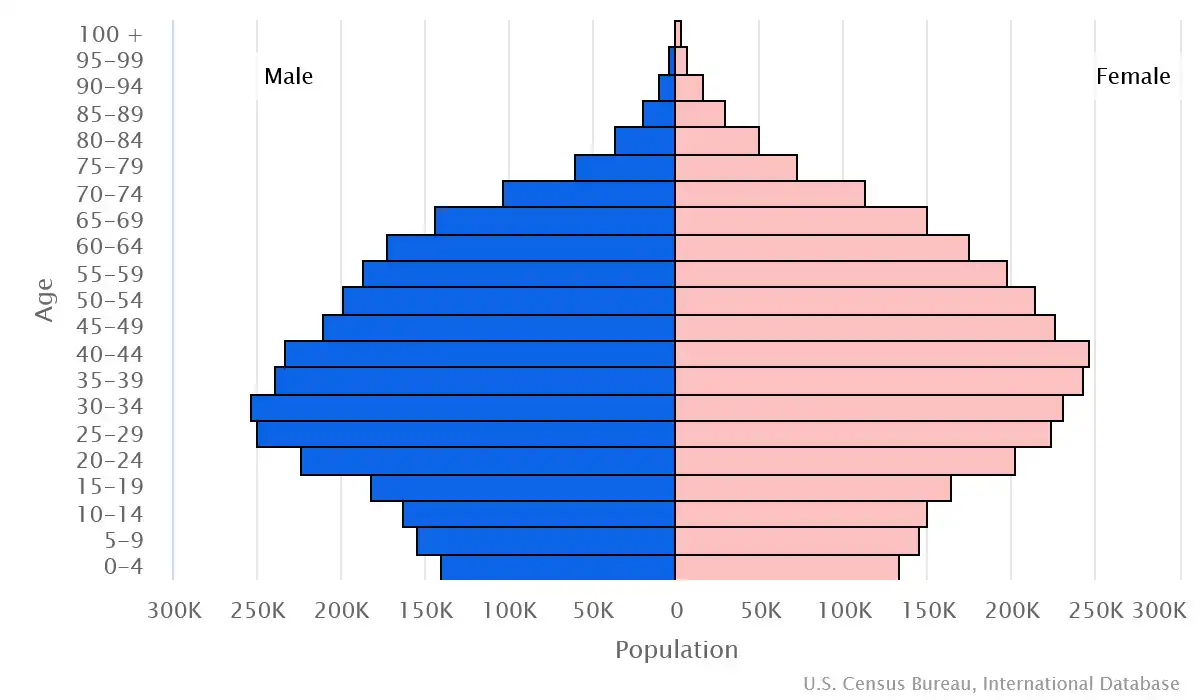
Age pyramid of Singapore
Singapore Economy Statistics
Economic overview of Singapore
high-income, service-based economy; global financial hub; business-friendly policies and open to investment and trade; inflation easing but persistent in services; public investments in education, healthcare, and infrastructure; strong human capital development challenged by aging population
Singapore Real GDP (purchasing power parity) in Billion $
Singapore Real GDP per capita in $
Singapore's Exports & Imports in billion $
Top 5 Import Partnerin 2022 (54%) of Singapore
Top 5 Import Commodities in 2022 of Singapore
- integrated circuits 💻
- refined petroleum ⛽
- crude petroleum 🛢️
- gold 💰
- machinery ⚙️
Top 5 Export Partnerin 2022 (50%) of Singapore
Top 5 Export Commodities in 2022 of Singapore
- integrated circuits 💻
- refined petroleum ⛽
- machinery ⚙️
- gold 💰
- gas turbines 🌀
Geography of Singapore
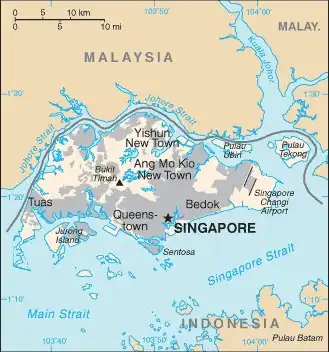
Map of Singapore
Land and Water Distrubtion of Singapore
Natural Resources of Singapore
- fish 🐟
- deepwater ports 💧
Climate inSingapore
tropical; hot, humid, rainy; two distinct monsoon seasons - northeastern monsoon (December to March) and southwestern monsoon (June to September); inter-monsoon - frequent afternoon and early evening thunderstorms
History of Singapore - a Summary
A Malay trading port known as Temasek existed on the island of Singapore by the 14th century. The settlement changed hands several times in the ensuing centuries and was eventually burned in the 17th century, falling into obscurity. In 1819, the British founded modern Singapore as a trading colony on the same site and granted it full internal self-government for all matters except defense and foreign affairs in 1959. Singapore joined the Malaysian Federation in 1963 but was ousted two years later and became independent. Singapore subsequently became one of the world's most prosperous countries, with strong international trading links and per capita GDP among the highest globally. The People’s Action Party has won every general election in Singapore since the end of the British colonial era, aided by its success in delivering consistent economic growth, as well as the city-state's fragmented opposition and electoral procedures that strongly favor the ruling party.
