
Spain Country Profile
Key Facts of Spain
| Government type: | parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
| Capital: | Madrid |
| Languages: | Castilian Spanish (official) 74%, Catalan (official in Catalonia, the Balearic Islands, and the Valencian Community) 17%, Galician (official in Galicia) 7%, Basque (official in the Basque Country and Navarre) 2%, Aranese (official in part of Catalonia) <5,000 speakers |
Spain Demographic Data
Ethnic Groups in Spain(2021 est.)
Religious Groups in Spain (2021 est.)
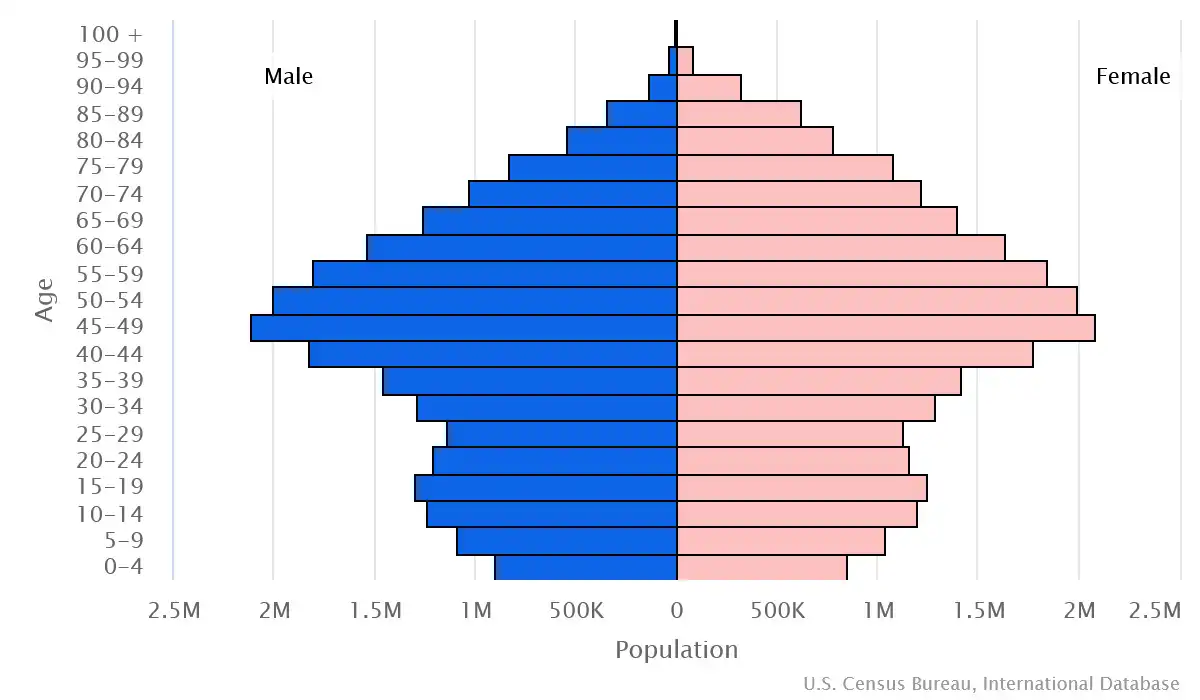
Age pyramid of Spain
Spain Economy Statistics
Economic overview of Spain
high-income core EU and eurozone economy; strong growth driven by public consumption, tourism, and other service exports; tight labor market despite high structural unemployment; government debt remains high amid deficit reductions; innovation and economic freedom ranked lower than EU and OECD peers
Spain Real GDP (purchasing power parity) in Billion $
Spain Real GDP per capita in $
Spain's Exports & Imports in billion $
Top 5 Import Partnerin 2022 (44%) of Spain
Top 5 Import Commodities in 2022 of Spain
- crude petroleum 🛢️
- natural gas 💨
- garments 👕
- cars 🚗
- vehicle parts/accessories 🛠️🚗
Top 5 Export Partnerin 2022 (50%) of Spain
Top 5 Export Commodities in 2022 of Spain
- cars 🚗
- refined petroleum ⛽
- garments 👕
- packaged medicine 💊
- vehicle parts/accessories 🛠️🚗
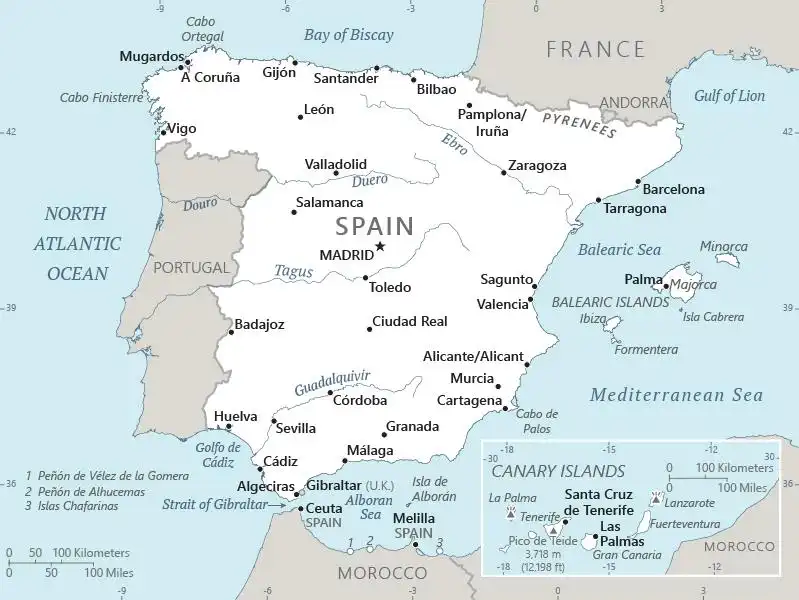
Geography of Spain
Map of Spain
Land and Water Distrubtion of Spain
Natural Resources of Spain
- coal ⚫
- lignite 🪨
- iron ore ⛓️
- copper 🟧🪙
- lead 🪙
- zinc 🔩
- uranium ☢️
- tungsten 🔧
- mercury ⚗️
- pyrites 🪙
- magnesite 🏔️
- fluorspar 💎
- gypsum ⚪🪨
- sepiolite 🪨
- kaolin 🪨
- potash 🪙
- hydropower 💧⚡
- arable land 🌱
Climate inSpain
temperate; clear, hot summers in interior, more moderate and cloudy along coast; cloudy, cold winters in interior, partly cloudy and cool along coast
History of Spain - a Summary
Spain's powerful world empire of the 16th and 17th centuries ultimately yielded command of the seas to England. Spain remained neutral during both World Wars but suffered through a devastating civil war (1936-39) resulting in a dictatorship. A peaceful transition to democracy after the death of dictator Francisco FRANCO in 1975 and rapid economic modernization after Spain joined the EU in 1986 gave Spain a dynamic and rapidly growing economy. After a severe recession in the wake of the global financial crisis in 2008, Spain has posted solid years of GDP growth above the EU average. Unemployment has fallen but remains high, especially among youth. Spain is the euro-zone's fourth-largest economy. The country has faced increased domestic turmoil in recent years due to the independence movement in its restive Catalonia region.
