
Switzerland Country Profile
Key Facts of Switzerland
| Government type: | federal republic (formally a confederation) |
| Capital: | Bern |
| Languages: | German (or Swiss German) (official) 62.1%, French (official) 22.8%, Italian (official) 8%, English 5.7%, Portuguese 3.5%, Albanian 3.3%, Serbo-Croatian 2.3%, Spanish 2.3%, Romansh (official) 0.5%, other 7.9% (2019 est.) |
Switzerland Demographic Data
Ethnic Groups in Switzerland(2020 est.)
Religious Groups in Switzerland (2020 est.)
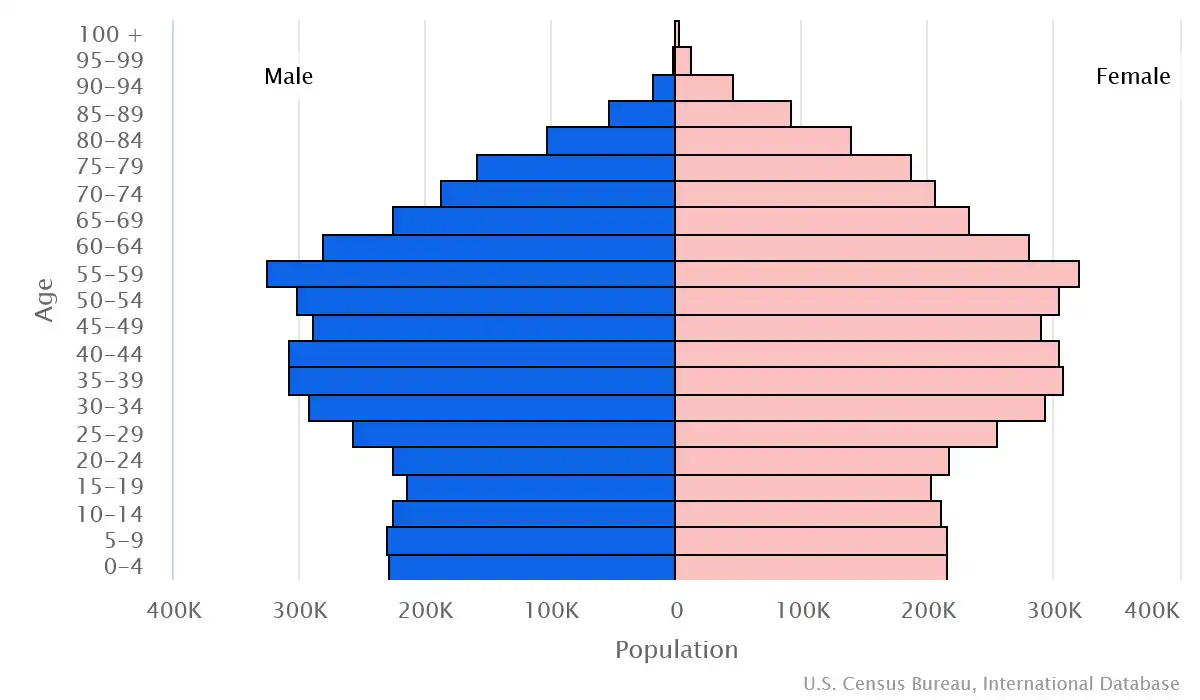
Age pyramid of Switzerland
Switzerland Economy Statistics
Economic overview of Switzerland
high-income, non-EU European economy; top ten in GDP per capita; renowned banking and financial hub; low unemployment and inflation; slowed GDP growth post-pandemic; highly skilled but aging workforce; key pharmaceutical and precision manufacturing exporter; leader in innovation and competitiveness indices
Switzerland Real GDP (purchasing power parity) in Billion $
Switzerland Real GDP per capita in $
Switzerland's Exports & Imports in billion $
Top 5 Import Partnerin 2022 (50%) of Switzerland
Top 5 Import Commodities in 2022 of Switzerland
- gold 💰
- packaged medicine 💊
- vaccines 💉
- cars 🚗
- garments 👕
Top 5 Export Partnerin 2022 (50%) of Switzerland
Top 5 Export Commodities in 2022 of Switzerland
- gold 💰
- vaccines 💉
- packaged medicine 💊
- nitrogen compounds 💨
- base metal watches ⌚
Geography of Switzerland
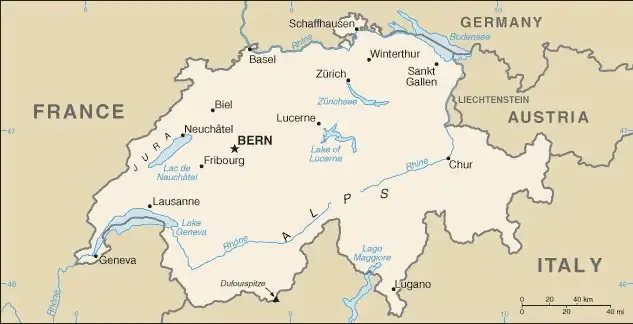
Map of Switzerland
Land and Water Distrubtion of Switzerland
Natural Resources of Switzerland
- hydropower potential 💧⚡
- timber 🌲
- salt 🧂
Climate inSwitzerland
temperate, but varies with altitude; cold, cloudy, rainy/snowy winters; cool to warm, cloudy, humid summers with occasional showers
History of Switzerland - a Summary
The Swiss Confederation was founded in 1291 as a defensive alliance among three cantons. In succeeding years, other localities joined the original three. The Swiss Confederation secured its independence from the Holy Roman Empire in 1499. A constitution of 1848, which was modified in 1874 to allow voters to introduce referenda on proposed laws, replaced the confederation with a centralized federal government. The major European powers have long honored Switzerland's sovereignty and neutrality, and the country was not involved in either World War. The political and economic integration of Europe over the past half-century, as well as Switzerland's role in many UN and international organizations, has strengthened Switzerland's ties with its neighbors. However, the country did not officially become a UN member until 2002. Switzerland remains active in many UN and international organizations but retains a strong commitment to neutrality.
