Tuvalu Country Profile
Key Facts of Tuvalu
| Government type: | parliamentary democracy under a constitutional monarchy; a Commonwealth realm |
| Capital: | Funafuti; note - the capital is an atoll of some 29 islets; administrative offices are in Vaiaku Village on Fongafale Islet |
| Languages: | Tuvaluan (official), English (official), Samoan, Kiribati (on the island of Nui) |
Tuvalu Demographic Data
Ethnic Groups in Tuvalu(2017 est.)
Religious Groups in Tuvalu (2017 est.)
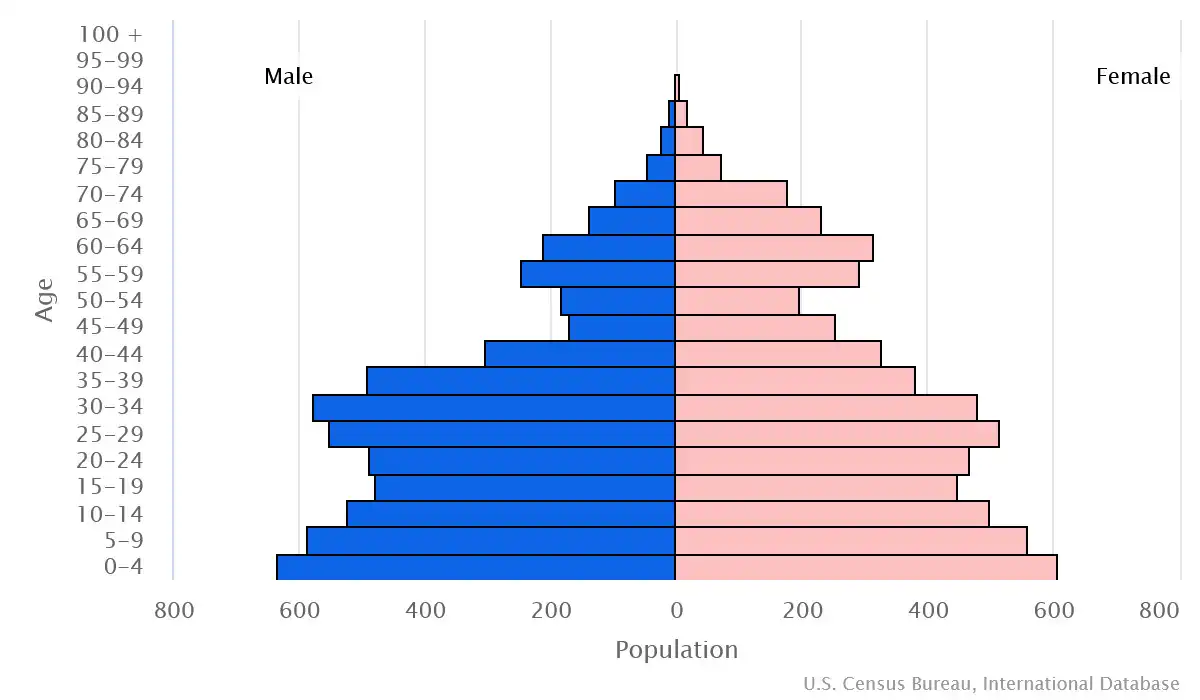
Age pyramid of Tuvalu
Tuvalu Economy Statistics
Economic overview of Tuvalu
upper middle-income Pacific island economy; extremely environmentally fragile; currency pegged to Australian dollar; large international aid recipient; subsistence agrarian sector; Te Kakeega sustainable development; domain name licensing incomes
Tuvalu Real GDP (purchasing power parity) in Billion $
Tuvalu Real GDP per capita in $
Tuvalu's Exports & Imports in million $
Top 5 Import Partnerin 2022 (91%) of Tuvalu
Top 5 Import Commodities in 2022 of Tuvalu
- ships 🚢
- refined petroleum ⛽
- iron structures 🛠️
- engine parts ⚙️
- plastic products ♻️
Top 5 Export Partnerin 2022 (97%) of Tuvalu
Top 5 Export Commodities in 2022 of Tuvalu
- fish 🐟
- ships 🚢
- computers 💻
- integrated circuits 💻
- nitrile compounds 💨
Geography of Tuvalu
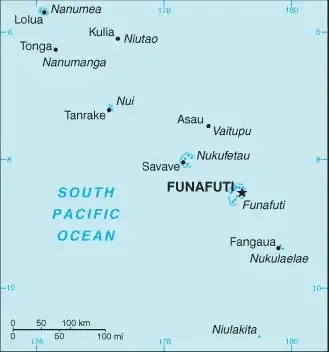
Map of Tuvalu
Land and Water Distrubtion of Tuvalu
Natural Resources of Tuvalu
- fish 🐟
- coconut (copra) 🥥
Climate inTuvalu
tropical; moderated by easterly trade winds (March to November); westerly gales and heavy rain (November to March)
History of Tuvalu - a Summary
Voyagers from either Samoa or Tonga first populated Tuvalu in the first millennium A.D., and the islands provided a stepping-stone for various Polynesian communities that subsequently settled in Melanesia and Micronesia. Tuvalu eventually came under Samoan and Tongan spheres of influence, although proximity to Micronesia allowed some Micronesian communities to flourish in Tuvalu, in particular on Nui Atoll. In the late 1700s and early 1800s, a series of American, British, Dutch, and Russian ships visited the islands, which were named the Ellice Islands in 1819.
The UK declared a protectorate over islands in 1892 and merged them with the Micronesian Gilbert Islands. The Gilbert and Ellice Islands Protectorate became a colony in 1916. During World War II, the US set up military bases on a few islands, and in 1943, after Japan captured many of the northern Gilbert Islands, the UK transferred administration of the colony southward to Funafuti. After the war, Tarawa in the Gilbert Islands was once again made the colony’s capital, and the center of power was firmly in the Gilbert Islands, including the colony’s only secondary school. Amid growing tensions with the Gilbertese, Tuvaluans voted to secede from the colony in 1974, were granted self-rule in 1975, and gained independence in 1978 as Tuvalu. In 1979, the US relinquished its claims to the Tuvaluan islands in a treaty of friendship.
