United Kingdom Country Profile
Key Facts of United Kingdom
| Government type: | parliamentary constitutional monarchy; a Commonwealth realm |
| Capital: | London |
| Languages: | English |
United Kingdom Demographic Data
Ethnic Groups in United Kingdom(2011 est.)
Religious Groups in United Kingdom (2011 est.)
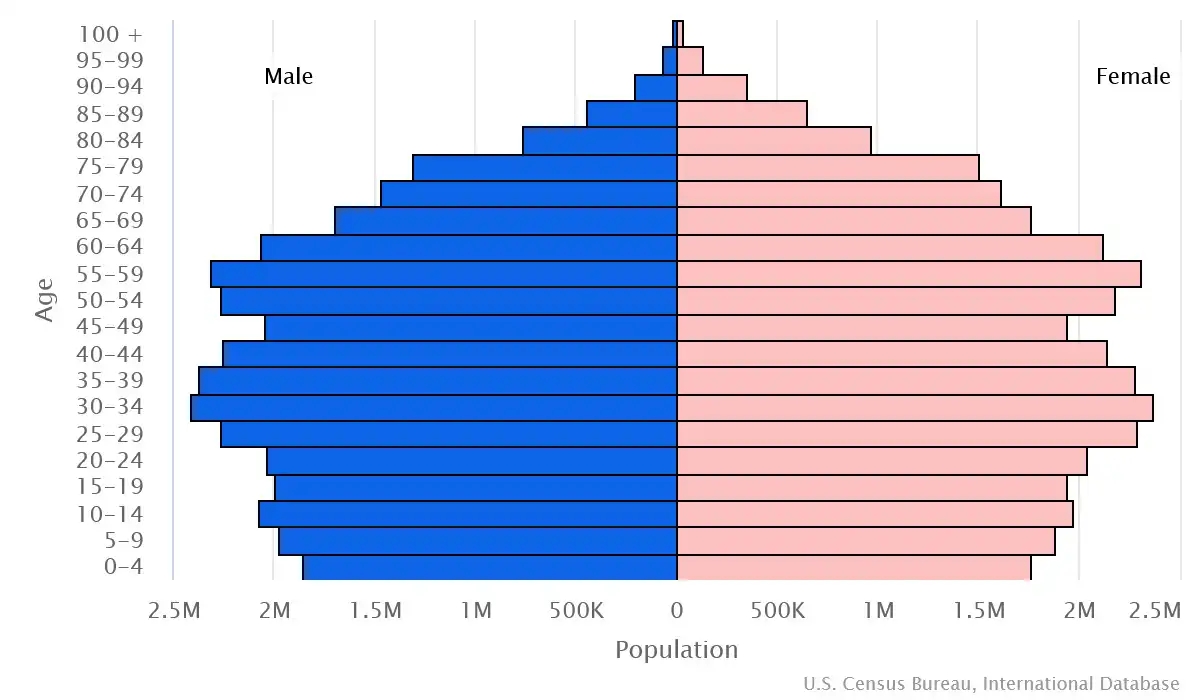
Age pyramid of United Kingdom
United Kingdom Economy Statistics
Economic overview of United Kingdom
high-income, non-EU European economy; global financial center and dominant service sector; sluggish growth from stringent monetary policy, reduced business investment, low productivity and participation rates; fiscal austerity in face of high public debt
United Kingdom Real GDP (purchasing power parity) in Billion $
United Kingdom Real GDP per capita in $
United Kingdom's Exports & Imports in trillion $
Top 5 Import Partnerin 2022 (45%) of United Kingdom
Top 5 Import Commodities in 2022 of United Kingdom
- natural gas 💨
- cars 🚗
- crude petroleum 🛢️
- gold 💰
- garments 👕
Top 5 Export Partnerin 2022 (46%) of United Kingdom
Top 5 Export Commodities in 2022 of United Kingdom
- gold 💰
- cars 🚗
- gas turbines 🌀
- crude petroleum 🛢️
- packaged medicine 💊
Geography of United Kingdom
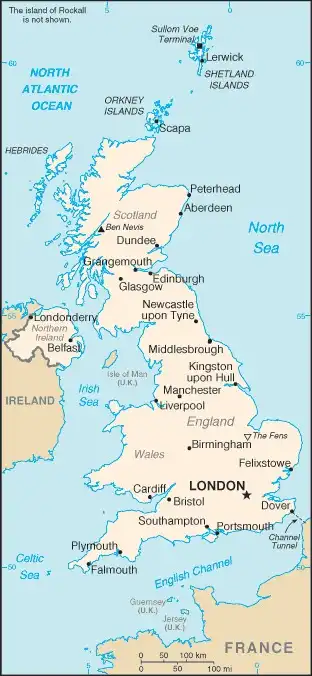
Map of United Kingdom
Land and Water Distrubtion of United Kingdom
Natural Resources of United Kingdom
- coal ⚫
- petroleum 🛢️
- natural gas 💨
- iron ore ⛓️
- lead 🪙
- zinc 🔩
- gold 💰
- tin 🪙
- limestone 🪨
- salt 🧂
- clay 🧱
- chalk ⚪🪨
- gypsum ⚪🪨
- potash 🪙
- silica sand 🏜️
- slate
- arable land 🌱
Climate inUnited Kingdom
temperate; moderated by prevailing southwest winds over the North Atlantic Current; more than one-half of the days are overcast
History of United Kingdom - a Summary
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland was created when the Kingdoms of England and Scotland -- which previously had been distinct states under a single monarchy -- were joined under the 1707 Acts of Union. The island of Ireland was incorporated under the 1800 Acts of Union, while Wales had been part of the Kingdom of England since the 16th century. The United Kingdom has historically played a leading role in developing parliamentary democracy and in advancing literature and science. The 18th and 19th centuries saw the rapid expansion of the British Empire despite the loss of the Thirteen Colonies, and at its zenith in the early 20th century, the British Empire stretched over one fourth of the earth's surface. The first half of the 20th century saw two World Wars seriously deplete the UK's strength and the Irish Republic withdraw from the union. The second half witnessed the dismantling of the Empire and the UK rebuilding itself into a modern and prosperous European nation. As one of five permanent members of the UN Security Council and a founding member of NATO and the Commonwealth of Nations, the UK pursues a global approach to foreign policy. The devolved Scottish Parliament, the National Assembly for Wales, and the Northern Ireland Assembly were established in 1998.
The UK was an active member of the EU after its accession in 1973, although it chose to remain outside the Economic and Monetary Union. However, motivated in part by frustration at a remote bureaucracy in Brussels and massive migration into the country, UK citizens in 2016 voted by 52 to 48 percent to leave the EU. On 31 January 2020, the UK became the only country to depart the EU -- a move known as "Brexit" -- after prolonged negotiations on EU-UK economic and security relationships.
